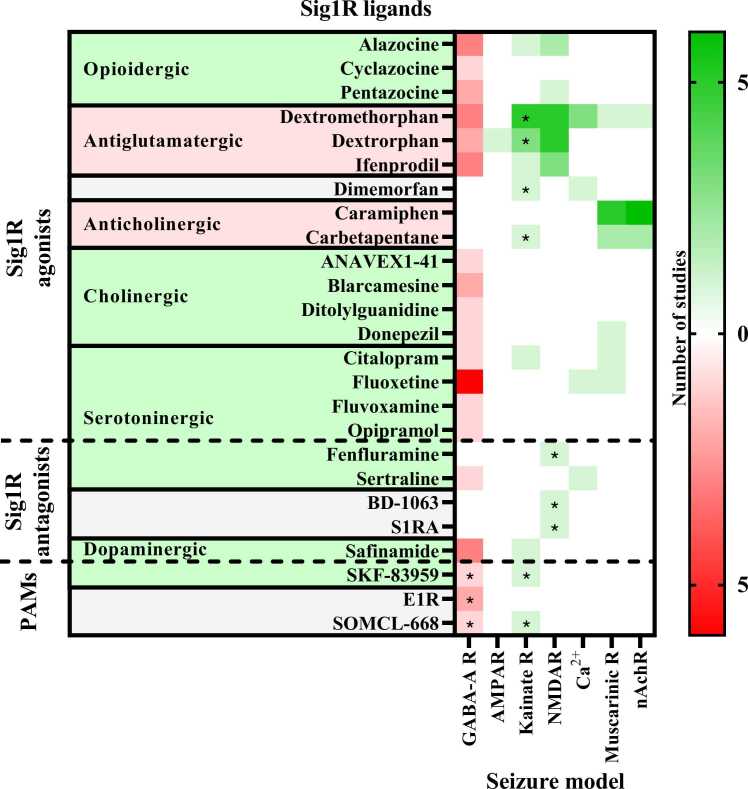
Fig. 2.
Anti-seizure activity profile of Sig1R ligands working against chemoconvulsant-induced seizures in vivo. Chemoconvulsants have been used to induce seizures either by inhibition (red) of the gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA)-A receptors or overactivation (green) of ionotropic glutamate receptors (AMPAR – α-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methylisoxazole-4-propionic acid receptors; Kainate R – kainate receptors; NMDAR – N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors), intracellular Ca2+ increase or acetylcholine receptors (Muscarinic R – muscarinic receptors; nAchR – nicotinic acetylcholine receptors). Asterisks indicate seizure models in which the anti-seizure effects of the Sig1R ligand has been confirmed to be Sig1R-dependent. PAMs – positive allosteric modulators of Sig1R. For more details see Table 1.