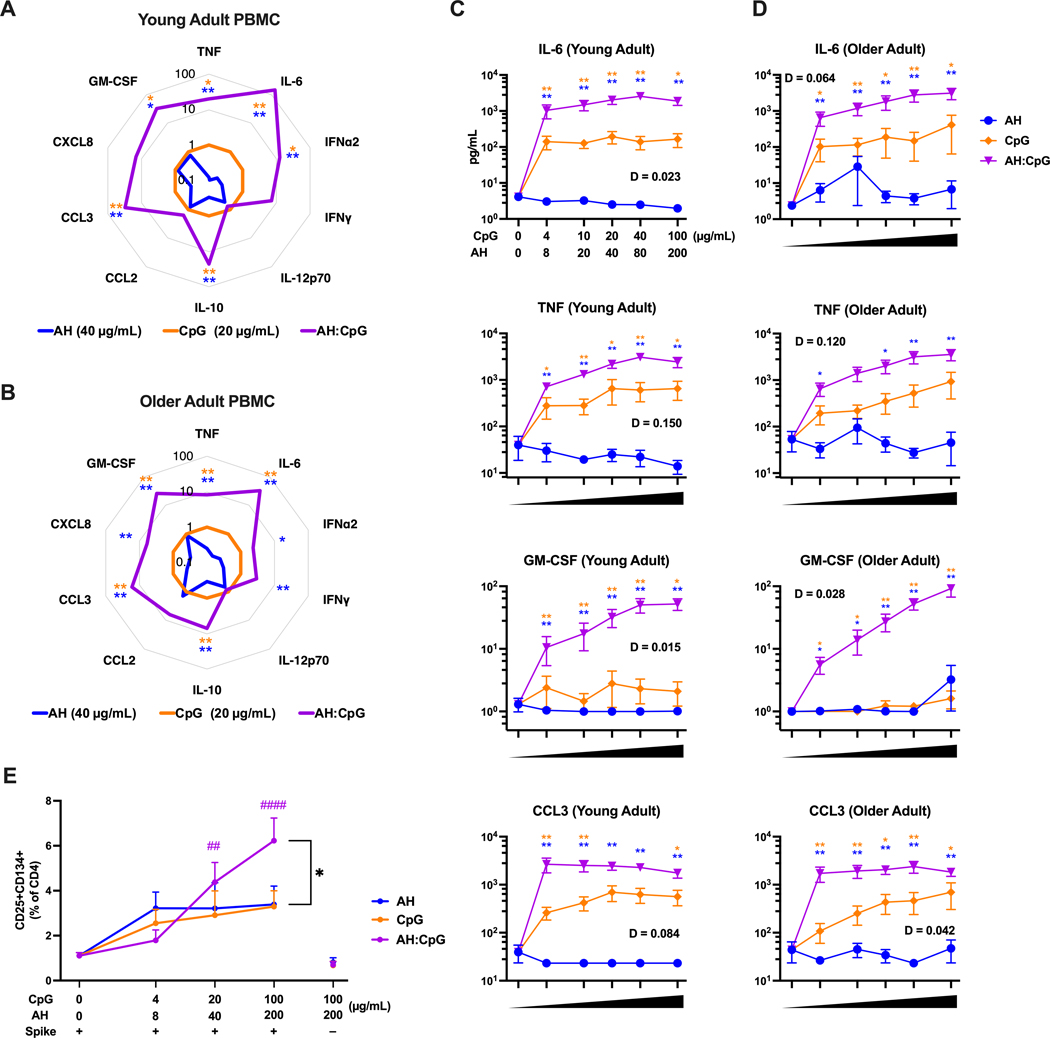
Figure 8. AH:CpG synergistically enhanced proinflammatory cytokine production from human PBMCs and enhanced MoDC-dependent memory T cell activation.
(A to D) Human PBMCs collected from young adults (A, C) and older adults (B, D) were cultured in vitro for 24 hours with CpG alone, aluminum hydroxide (AH) alone, or a combination of both. Supernatants were collected for multiplexing bead array. n=6 per age group. (A and B) Radar plot analysis presented as a fold-change over the CpG alone group for the 20 μg/mL CpG and 40 μg/mL AH conditions. (C and D) Cytokine and chemokine concentrations are shown at the indicate doses of CpG and AH. Results are presented as mean ± SEM. Unpaired Mann-Whitney tests were applied at each concentration. Blue and yellow colored asterisks indicate comparisons of AH:CpG formulation to AH and CpG alone groups, respectively. Degree of synergy was calculated using an adapted Loewe definition of additivity (D <1: synergy, D=1: additivity, D >1: antagonism). (E) Human monocyte-derived dendritic cells from young adults were stimulated with spike protein and indicated adjuvants and co-cultured with CD4+ T cells for 5 days. The percent of CD25+CD134+ CD4+ T cells of total CD4+ T cells was assessed. n=5. Results are presented as mean ± SEM. Statistical significance was determined by two-way repeated measures ANOVA corrected for multiple comparisons. * indicates comparisons among AH, CpG, and AH:CpG at the same concentration. # indicates comparisons among same adjuvant groups to the baseline control (antigen only). Comparisons among experimental groups are indicated by color code. * P <0.05, **/ ## P <0.01, #### P <0.0001.