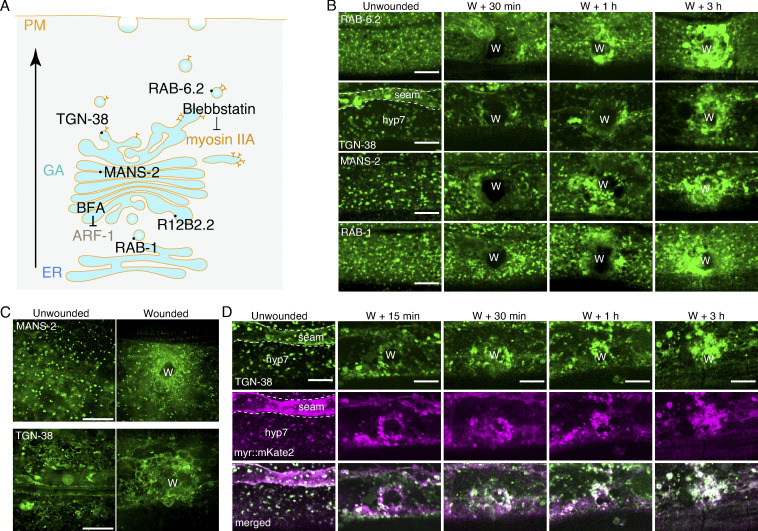
Figure 3.
Wounding triggers the accumulation of the Golgi membrane at the wound site. (A) Diagram showing the location of Golgi apparatus compartment markers and the target of pharmacological inhibitors. (B) Representative confocal images showing the distribution of Golgi apparatus markers before and after wounding. The markers include GFP::RAB-1 (ERGIC), GFP::MANS-2 (medial), GFP::RAB-6.2 (trans), and TGN-38::tagBFP (TGN), respectively. Pcol-19-GFP::RAB-6.2(zjuSi313), Pcol-19-TGN-38::tagBFP(zjuSi280), Pcol-19-GFP::MANS-2(zjuSi302), and Pcol-19-GFP::RAB-1(zjuSi253) transgenic animals were used for wounding and imaging. “W” indicates the wound site. Scale bar: 10 µm. (C) HiS-SiM single-plane images showing the accumulation of TGN-38::tagBFP and GFP::MANS-2 at the wound site. Pcol-19-TGN-38::tagBFP(zjuSi280) and Pcol-19-GFP::MANS-2(zjuSi302) transgenic animals were used for wounding and imaging. Scale bar: 10 µm. (D) Representative single-plane confocal images showing the colocalization of TGN-38::tagBFP and myr::mKate2 before and after wounding. Pcol-19-TGN-38::tagBFP(zjuSi280); Pcol-19-myr::mKate2(zjuSi46) transgenic animals were used for wounding and imaging. “W” indicates the wound site. Scale bar: 10 µm. See also Fig. S3 and Video 9.