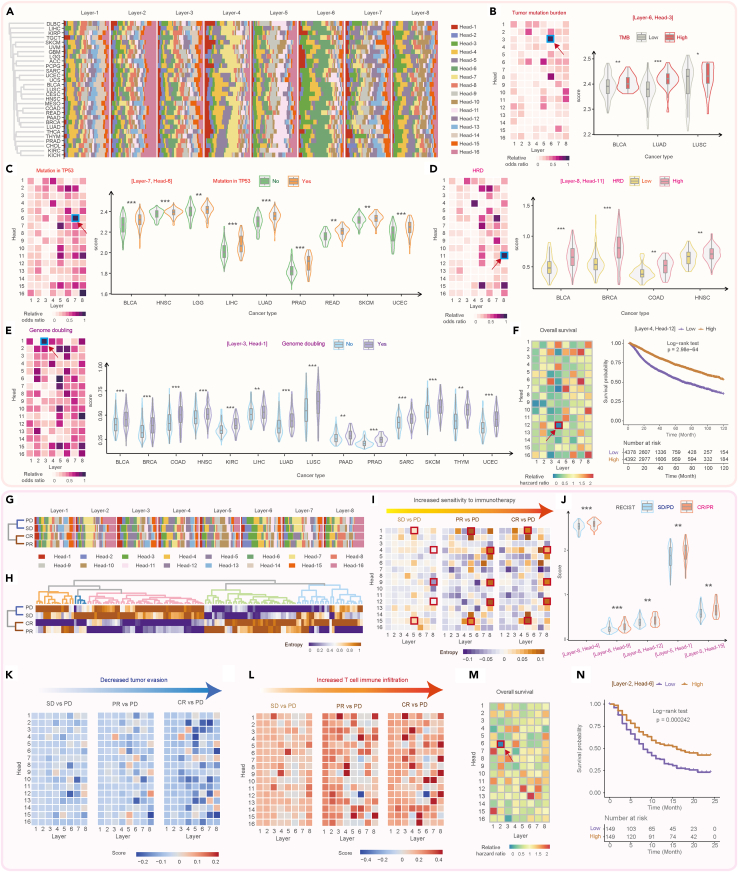
Figure 5.
The association of features learned by tGPT versus genomic alteration events and clinical phenotype
(A) Heatmap representation of attention head importance score across different cancer types on the TCGA dataset.
(B–F) Association of attention head entropy versus tumor mutation burden (B), TP53 mutation (C), homologous recombination deficiency (D), genome doubling (E) and overall survival (F) on the TCGA cohort.
(G and H) Heatmap representation of attention head importance and entropy on the urothelial carcinoma stratified by RECIST response. CR, complete response; PR, partial response; SD, stable disease; PD, progress disease.
(I) The varying entropy patterns from SD to PR to CR with PD as baseline.
(J) Exemplified violin plots depicting attention head entropy in SD/PD versus CR/PR.
(K) The varying of patterns of tumor evasion signature from SD to PR to CR with PD as baseline.
(L) The varying of patterns of T cell infiltration signature from SD to PR to CR with PD as baseline.
(M) Association between attention head entropy and overall survival on the urothelial carcinoma dataset.
(N) Exemplified survival curves stratified by attention head entropy.