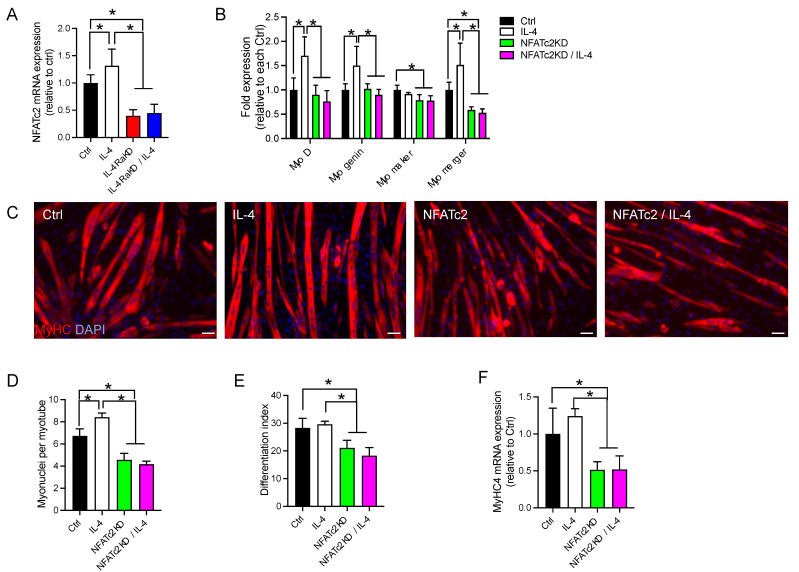
Figure 6.
Knockdown of NFATc2 abolished the effects of activation of the IL-4/IL-4Rα signaling pathway in C2C12 cells. (A) IL-4 treatment promoted the expression of NFATc2 mRNA. Fold changes in the mRNA levels of NFATc2 are shown. (B) Knockdown of NFATc2 significantly suppressed the increased expression of MyoD, myogenin, myomaker, and myomerger. The fold changes of their mRNA levels are shown. For the experiments in (A,B), C2C12 cells were transfected with control siRNA (Ctrl) and IL-4Rα siRNA (IL-4RαΚD) or NFATc2 siRNA (NFATc2KD) and were grown in GM for 24 h. The medium was replaced by DM with or without recombinant IL-4 (10 ng/mL), and the cells were maintained for 72 h. Total RNA was extracted and subjected to qRT-PCR analysis. N = 3–4 per group. (C) Representative immunofluorescence images of MyHC (red) in the NFATc2KD C2C12 myoblasts. Cell nuclei were counterstained with DAPI (blue). Myotube formation was inhibited in the NFATc2KD C2C12 cells. In this experiment, cells were treated as described above. Scale bars: 50 μm. (D–F) The number of myonuclei per myotube, the differentiation index, and fold changes of MyHC4 mRNA are shown in (D–F), respectively. These three parameters of myoblast fusion and differentiation were significantly decreased by NFATc2 knockdown. N = 3–4 per group. Data represent mean ± SD. * p < 0.05.