Extended Data Fig. 3 |. Generation of mutations in functional domains of Halo-GAF by CRiSPR/Cas9 gene editing.
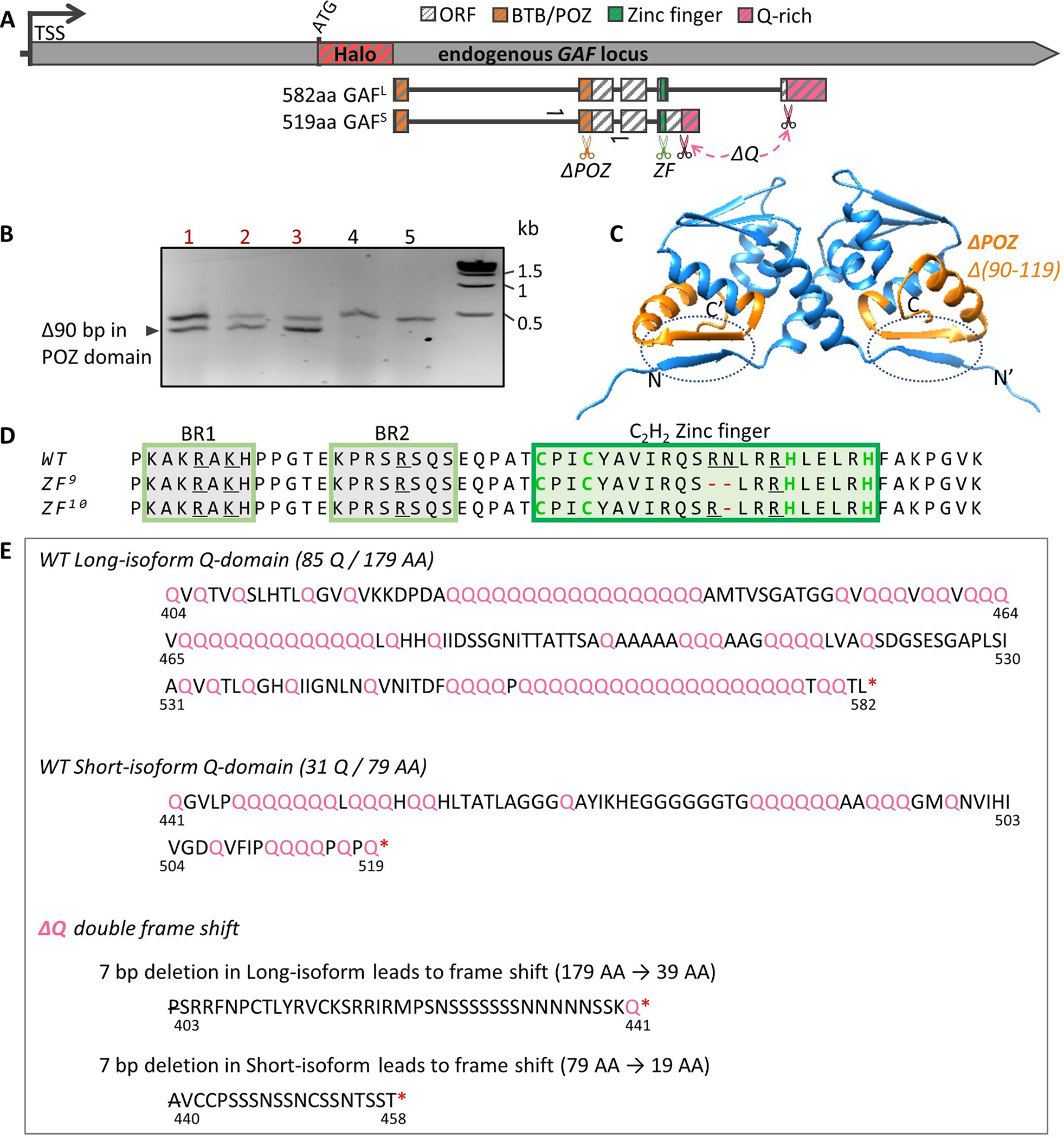
(A) In the Halo-GAF fly strain, Cas9 and gRNA were introduced to target the BTB/POZ domain, zinc finger and Q-rich domains, respectively. The BTB/POZ domain is separated by a large intron. A gRNA target site in the second exon (orange scissors) was selected and a donor plasmid containing a 90 bp deletion (ΔPOZ) was constructed for homology-directed repair (HDR). For zinc finger mutations, we selected a gRNA target site in the zinc finger coding region (green scissors) and screened for in-frame small deletions generated by non-homologous end joining (NHEJ). To generate deletions of both Q-rich domains in long and short isoforms (ΔQ), two gRNAs targeting the upstream ends of two Q-rich domains (pink scissors) were introduced at the same time, and we screened for double frame-shift deletions induced by NHEJ. Half arrows indicate positions of the PCR primers used in (B). TSS, transcription start site. (B) PCR validation of ΔPOZ. Lanes 1–3 show two PCR bands indicating precise deletion in one allele; lanes 4–5 are two lines without the precise deletion. Sanger sequencing verified a precise 90 bp deletion in one allele. (C) AlphaFold121 predicted structure for a homodimer of GAF POZ domains (residues 1–120) is highly similar to published crystal structures of PLZF POZ domains122,123. A 90-bp deletion in the second exon generates a 30-AA deletion (Δ90–119, ΔPOZ, orange), which includes a sheet that mediates two of three principal contacts stabilizing the dimer (dashed circles). This functionally lethal mutation is likely to impair GAF multimerization, although the degree to which the multimerization is reduced is unclear. N and C indicate two termini of one monomer; N’ and C’ for the other monomer. (D) Amino acid sequence of GAF DNA binding domain, which contains a single C2H2 zinc finger (green rectangle) and two upstream basic regions (BR1 and BR2, yellow rectangle). Amino acids involved in recognizing the GAGAG consensus sequence are underlined56. Two zinc finger mutations were isolated and verified by sanger sequencing, ZF9 and ZF10, with R356 and N357, or R356 deleted, respectively. (E) Amino acid sequence of GAF Q-rich domains for long and short isoforms. In ΔQ, a 7 bp deletion was identified by sanger sequencing in both isoforms at the upstream ends of Q-rich domains, resulting in frameshifts and truncations of the Q-rich domains from both isoforms. P403 in the long isoform and A440 in the short isoform are deleted and the subsequent amino acids are newly introduced by the frame shifts.
