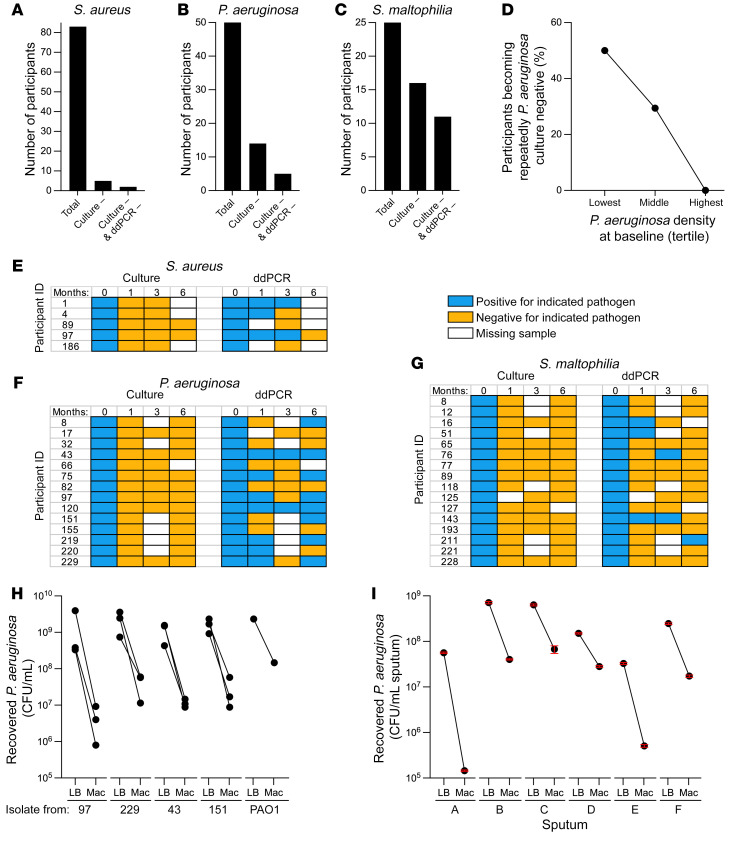
Figure 3. Some participants become repeatedly culture negative for CF pathogens after ETI.
(A–C) The number of participants with sputum cultures positive for Staphylococcus aureus (A), Pseudomonas aeruginosa (B), or Stenotrophomonas maltophilia (C) at the baseline visit who provided at least 2 post-ETI samples are indicated as “Total”. The number of participants whose sputum became repeatedly culture negative (i.e., all samples after the baseline visit were culture negative) for the indicted pathogen are indicated as “Culture –”. The number of participants whose sputum became repeatedly culture and ddPCR negative (i.e., all samples after the baseline visit were culture and ddPCR negative) are indicated as “Culture – & ddPCR –”. (D) Inverse relationship between P. aeruginosa sputum culture density at the baseline visit and transition to repeatedly P. aeruginosa culture–negative status after ETI. Baseline P. aeruginosa culture density was categorized by tertile; the highest tertile exceeded 1.08 × 107, middle was between 1.08 × 107 and 4.21 × 104, and lowest was less than or equal to 4.21 × 104 P. aeruginosa CFU/gm of sputum. Significance of differences was significant by Fisher’s exact test, P = 0.005. See Supplemental Table 8 for the number of participants analyzed and statistical analysis. (E–G) ddPCR assays detect pathogens in some culture-negative sputum samples. Participants becoming repeatedly culture negative for S. aureus (E), P. aeruginosa (F), or S. maltophilia (G) are indicated in rows and results of pathogen detection by culture and ddPCR are indicated by study time point in columns. Positive culture or ddPCR results are indicated in blue; negative culture or ddPCR results are indicated in yellow; missing data are indicated by white. See Supplemental Figure 7 for results of ddPCR assays in participants culture positive for P. aeruginosa and S. aureus. (H and I) Selective media used for P. aeruginosa culture reduced recovery of P. aeruginosa. Three isolates each from 4 PROMISE participants and the reference strain PAO1 (H) grown to late stationary phase, and sputum from 6 people with CF (I) were cultured on nonselective LB agar (LB) or the selective MacConkey agar (Mac) used for sputum P. aeruginosa culture in this study and by clinical labs generally, and viable P. aeruginosa counts measured (see Methods). CFU recovered from LB was higher than CFU recovered from MacConkey (P < 0.05 for all samples) by multiple unpaired, 2-tailed t tests on log-transformed values.