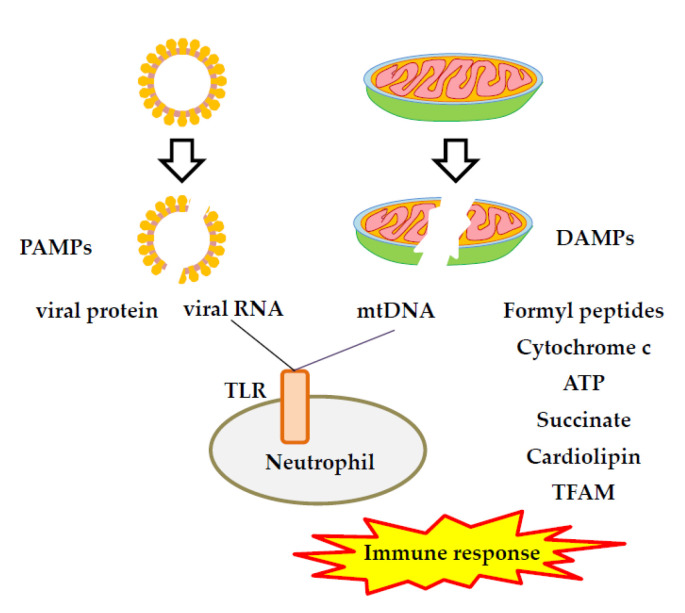
Figure 1.
Mitochondrial damage-associated molecular patterns (DAMPs) and related pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs) in the chronic inflammasome. Inflammation is caused by damage or infection by stimulatory signals, including PAMPs and DAMPs. PAMPs are derived from microbial products such as viral nucleic acids, which trigger inflammation in response to infection. DAMPs originate from host cells or products released by cells in response to signals such as hypoxia, producing sterile inflammatory responses in settings such as myocardial infarction, cancer, autoimmune disease, and atherosclerosis. ATP, adenosine triphosphate; DAMPs, damage-associated molecular patterns; mtDNA, mitochondrial DNA; TFAM, transcription factor A mitochondria; TLR, toll-like receptor.