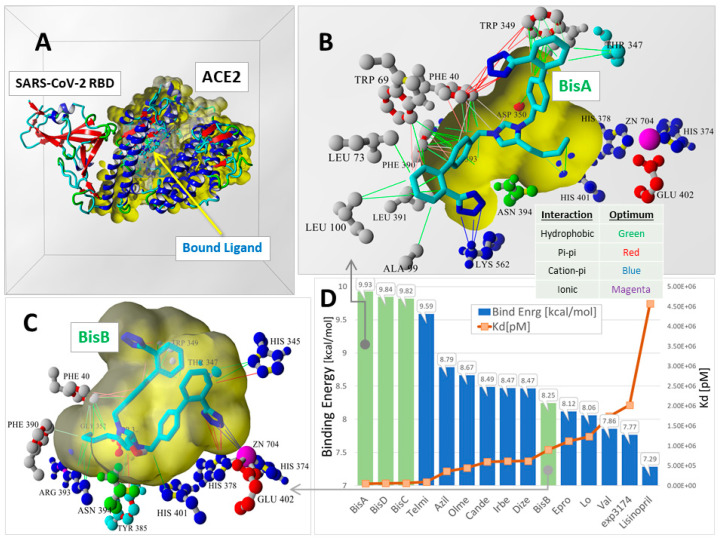
Figure 3.
Global docking of 15 ARBs to the 6LZG ACE2-SARS-CoV-2 RBD complex by Ridgway et al. [22]. Docking was performed using AutoDock VINA (YAMBER3 force field) with 100 runs for each ARB. The docking domain comprised a rectilinear cell with non-periodic (wall) boundaries 8 Å from any target atom. (A) Overview of 6LZG showing the major ACE2 channel where ARBs preferentially underwent docking. (B) The binding motif of bisartan BisA involved hydrophobic (green lines), pi–pi-resonance (red lines), and cation–pi (blue lines) interactions. Although the BisA conformational pose shown was proximate to the Zn2+ cofactor and also exhibited the strongest binding (9.93 kcal/mol) compared to all other ARBs, it did not directly coordinate with the Zn2+ cofactor. (C) The binding motif of BisB (8.25 kcal/mol) underwent coordination with Zn2+ via pi–pi resonance (red lines) and cation-pi (blue lines) interactions. (D) VINA docking scores (bars) and dissociation constants (Kd; orange line) were calculated for the best poses of all 15 ARBs. With the exception of BisB, the bisartans (green-shaded bars) consistently exhibited stronger ACE2 binding compared to all other ARBs.