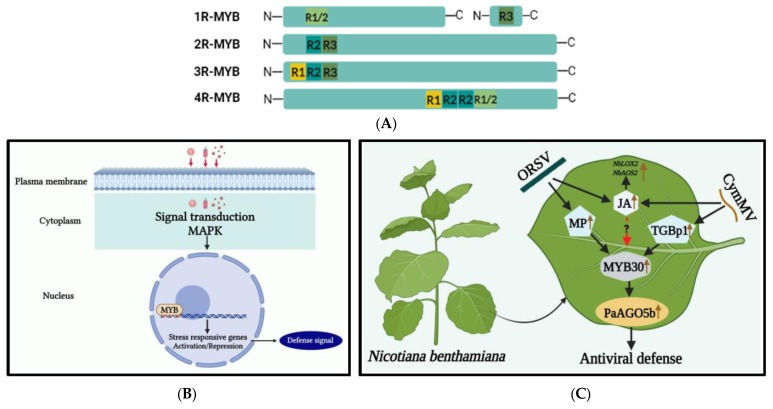
Figure 3.
(A) Illustration of the classification and structure of myeloblastosis-related (MYB) TFs in plants. MYB TFs with one to four MYB domain repeats that are identified in plants. (B) Mechanism of MYB TFs under viral stress. During viral stress, a cascade of signaling mechanisms, leading to plant defense responses, is triggered as modulation of very long fatty acid chains takes place, mounting a HR response within the plant cell. MYB TF interacts with promoter elements of defense-related genes, which plays a crucial role in this response. (C) A model for enhancing antiviral defense mechanisms through the activation of the Phalaenopsis aphrodite subsp. formosana argonaute 5b promoter (pPaAGO5b). The Cymbidium mosaic virus (CymMV) and the Odontoglossum ringspot virus (ORSV) infectious clones and their triple gene block protein 1 (TGBp1), a CymMV-encoded protein, and movement protein (MP), an ORSV-encoded protein, may up-regulate plant defense-related NbMYB30. The NbMYB30 binds to the pPaAGO5b (p-indicates the promoter) and transcriptionally activates PaAGO5b expression to strengthen the antiviral defense mechanism. During viral infection, the phytohormone JA and related marker genes (NbLOX2 and NbAOS2) were upregulated. LOX2-lipoxygenase 2; AOS2-allene oxide synthase 2 [79].