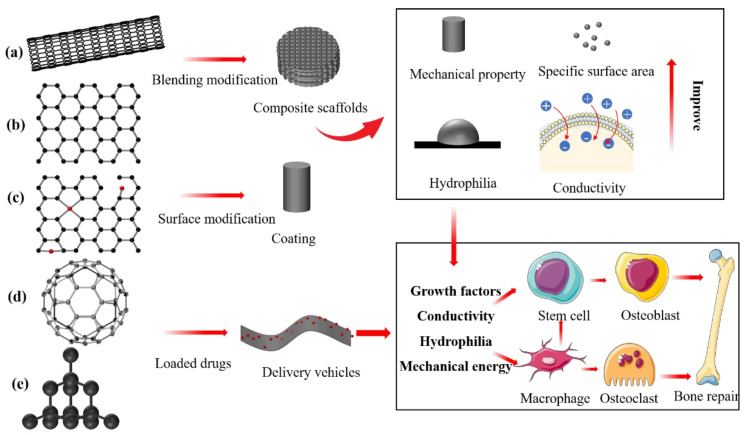
Figure 4.
Schema of molecular structure of carbon-based family nanomaterials. (a) Carbon nanotubes. (b) Graphene. (c) Reduced graphene oxide. (d) Fullerenes. (e) Nanodiamonds. These carbon-based nanomaterials can be prepared into bone-repair scaffolds with various properties or loaded with bioactive factors and directly (growth factors) or indirectly (conductive or hydrophilically) promote bone tissue regeneration.