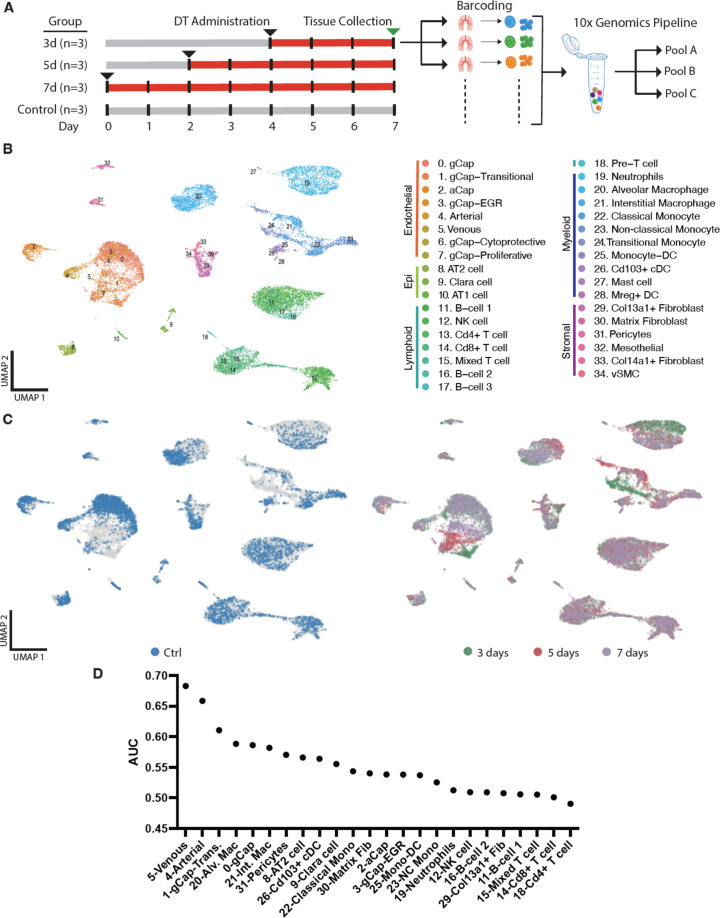
Figure 3. Multiplexed single-cell transcriptomic analysis after diphtheria toxin (DT)-induced lung endothelial cell (EC) ablation.
(A) Schematic of workflow showing the experimental design. Three separate cohorts (3, 5, and 7 days) of binary transgenic mice received DT (IT, 10 ng), and a fourth cohort of healthy animals served as a control, with the timing of DT delivery such that all mice were sacrificed on the same day. Three animals (biological replicates) were included per group. Lungs cells were immediately isolated and barcoded to identify individual donor animals, then pooled and subjected to library construction using 10x-Genomics Single-cell 3’ RNA sequencing kit v.3. Global plot of all lung cells at all time points using uniform manifold approximation and projection (UMAP). (B) 35 distinct populations were identified and could be assigned into five major categories: endothelial, epithelial stromal, myeloid, and lymphoid. (C) UMAP plots of global lung cells are shown for each mouse cohort: control (blue); day 3 (green), day 5 (red), and day 7 (purple) (C). (D) A machine learning model was used to predict cells that become more separable during treatment based on their molecular measurements (Skinnider and Lin, 2021; Skinnider et al., 2021). More details for this analysis are provided in Figure 3—figure supplements 1–2.