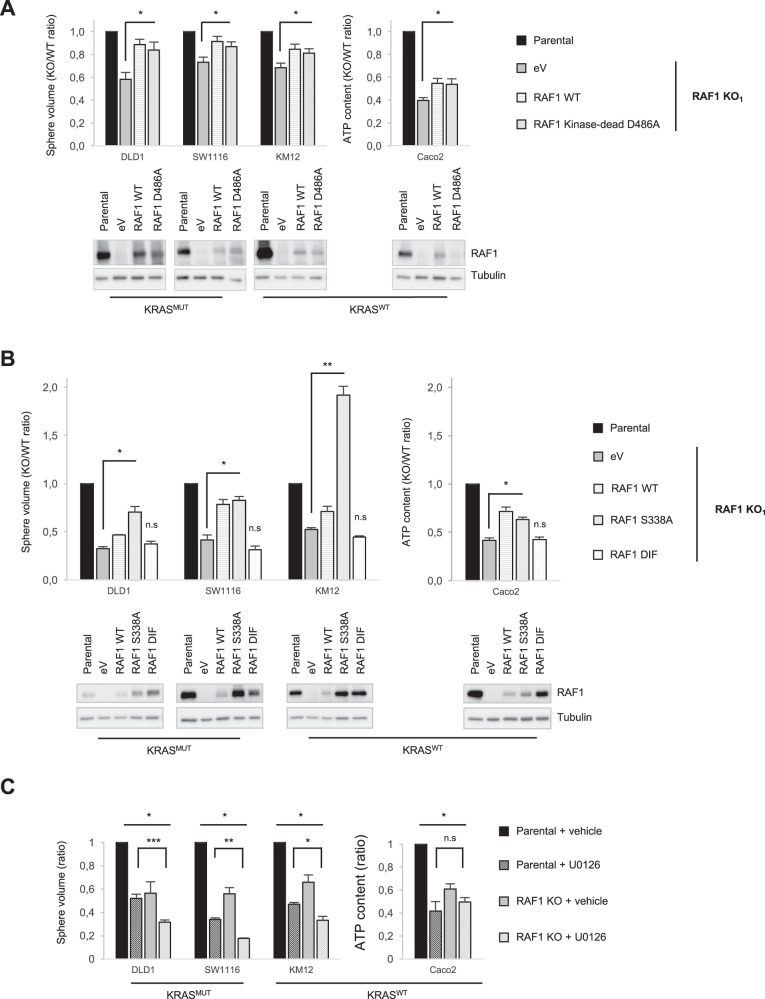
Fig. 3. RAF1 kinase activity is dispensable for proliferation while intact dimerization is required, and RAF1 loss combined with MEK inhibition strongly affects CRC cells.
A RAF1 KO cell lines were stably transfected with either an empty vector (eV), RAF1 full length (WT) or the RAF1 kinase-dead mutant D486A. Spheroid volume or ATP content were determined 5 days after spheroid formation. The parental cell lines were compared with their respective RAF1 KO1 clone reconstituted with empty vector or with the RAF1 constructs. The experiment was repeated at least three times (top panel). The Western blot shows RAF1 expression compared to the parental cell lines. Tubulin was used as a loading control (bottom panel). B RAF1 KO cell lines were stably transfected with either an empty vector (eV), RAF1 full length (WT), the phosphoablative mutant S338A, or the DIF mutant which unables dimerization. Spheroid volume or ATP content were measured 5 days after spheroid formation. The parental cell lines were compared with their respective RAF1 KO1 clone reconstituted with empty vector or RAF1 constructs. The experiment was performed three times (top panel). Immunoblot shows RAF1 expression compared to the parental cell lines. Tubulin was used as a loading control (bottom panel). C Parental and RAF1 KO spheroids were treated for 5 days with either DMSO (vehicle), 10 µM U0126 (DLD1, SW116 and Caco2) or 1 µM U0126 (KM12). Spheroid volume or ATP content was determined at the end of the experiment. The plot represents the mean of three independent RAF1 KO clones.The experiment was performed at least three times. A–C, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, n.s not significant.