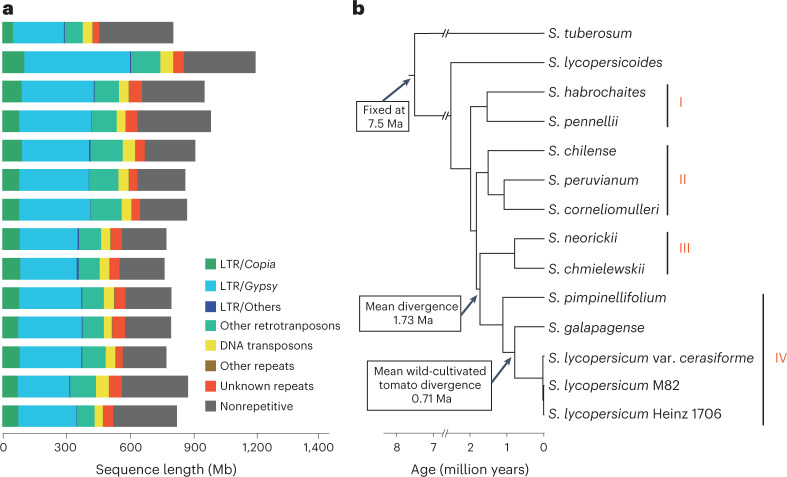
Fig. 1. Phylogenetic relationships and genomic components of wild and domesticated tomatoes.
a, TE content in genomes of potato and the 13 wild and cultivated tomatoes. The order of species is corresponding to the phylogeny shown in b. b, Species phylogeny of ten species (13 genomes) from Solanum sect. Lycopersicon and Solanum sect. Lycopersicoides using S. tuberosum as the outgroup. The 12 Lycopersicon genomes are clustered into four clades.