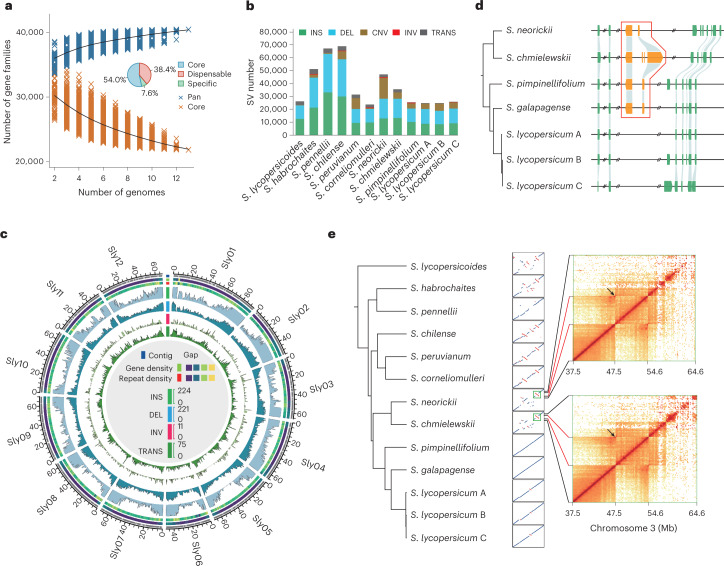
Fig. 2. Super-pangenome and the landscape of structural variation among wild and cultivated tomatoes.
a, Modeling of pangenome and core-genome sizes when incorporating additional genomes into clustering and composition of the tomato super-pangenome (pie chart). b, Number of different types of structural variants within each genome compared with the S. galapagense reference genome. c, Distribution of structural variants from the 12 tomato genomes across the 12 chromosomes. d, A wild-specific genomic fragment on chromosome 1. An 8-kb sequence was present in genomes of all nine wild tomatoes but absent from the three domesticated tomatoes. The 8-kb wild-specific region harboring two genes is outlined in red. e, Dot plots display the alignments of chromosome 3 between the 12 tomato genomes and the S. galapagense genome. A clade IV-specific inversion on chromosome 3 from 47.5 Mb to 54.6 Mb is shown, as evidenced by abnormally strong interactions around the inversion breakpoints in Hi-C heat maps. In b, d and e, S. lycopersicum A, S. lycopersicum var. cerasiforme. S. lycopersicum B, S. lycopersicum var. lycopersicum cv. M82. S. lycopersicum C, S. lycopersicum var. lycopersicum cv. Heinz 1706. DEL, deletion; INS, insertion; INV, inversion; TRANS, translocation.