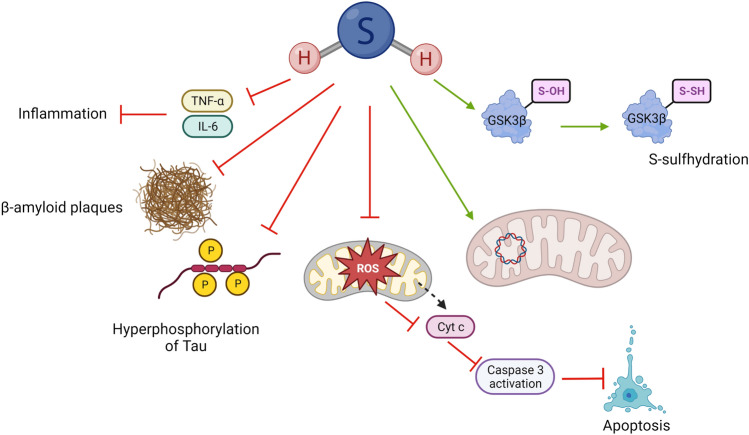
Fig. 4.
Protective mechanisms of H2S in AD. The neuroprotective effects of H2S in AD are associated with inhibition of anti-inflammatory cascade via reduction of TNF-β and IL-6 levels. Moreover, H2S has been linked to reduction of size of β-amyloid plaques and reduction in hyperphosphorylation of Tau. H2S has been observed to reduce levels of mitochondrial reactive oxygen species (ROS) leading to inhibition of apoptosis via caspase 3. H2S may also maintain the integrity of mitochondrial DNA whilst it may also regulate GSK3β protein functions via S-sulfhydration (persulfidation)