Figure 1.
Laterality defects induced by early removal of archenteron fluid
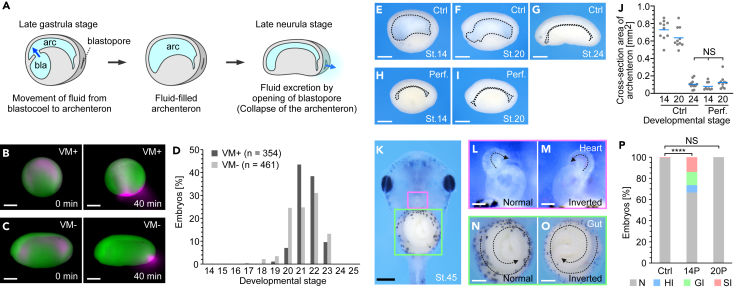
(A) Schematic of extracellular fluid transport in Xenopus embryos. bla, blastocoel; arc, archenteron.
(B and C) Snapshot images from representative time-lapse imaging of fluid excretion in embryos with (B; n = 8) or without (C; n = 6) the vitelline membrane (VM). Cells, green; extracellular fluid, magenta. Scale bars = 500 μm.
(D) Measurement of fluid excretion stages. VM+, n = 354; VM-, n = 461.
(E-I) Sagittal section of control embryos (Ctrl; E-G) and perforated embryos (Perf.; H, I). The black dotted line outlines the archenteron. Scale bars = 500 μm.
(J) Cross-section area of the archenteron in (E-I): Control embryos at stage 14 (n = 10), stage 20 (n = 10), and stage 24 (n = 12). Perforated embryos at stage 14 (n = 9) and stage 20 (n = 10). Blue lines, mean.
(K-O) Ventral view of embryos at stage 45. Magenta and green squares indicate the heart and gut, respectively (K). Magnified view of normal (L) and inverted (M) heart. Magnified view of normal (N) and inverted (O) gut. Scale bars = 500 μm (K), 100 μm (L, M), 300 μm (N, O).
(P) Ratio of normal and laterality defects. Control embryos (Ctrl; n = 176). Embryos perforated at stage 14 (14P; n = 48) or stage 20 (20P; n = 59). N, normal; HI, heart inverted; GI , gut inverted; SI, situs inversus. ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001. n = number of animals used. See also Video S1.