Figure 5.
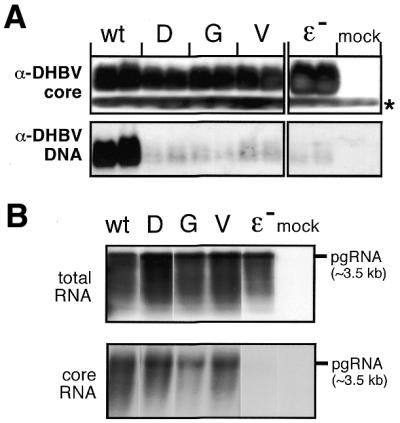
P protein variants in the context of complete DHBV genomes. (A) DHBV nucleocapsid formation. LMH cells were transfected with expression plasmids for DHBV genomes encoding wild-type P protein, the indicated variants, an encapsidation-deficient construct (ɛ–) or with empty plasmid vector (mock). Equal aliquots from cytoplasmic lysates were analyzed in duplicate by native agarose gel electrophoresis. After blotting DHBV core protein was detected using an anti-DHBV capsid antiserum (top) and a secondary antibody-peroxidase conjugate, followed by a chemiluminescent substrate. The faster migrating band (asterisk) corresponds to a non-specific cross-reaction product. DHBV DNA was detected by Southern hybridization using a DIG-labeled DNA probe (bottom) and a chemiluminescent substrate. (B) Encapsidation competence of variant DHBV P proteins. Capsids were enriched from cytoplasmic lysates of LMH cells transfected with the indicated constructs by immunopreciptiation with anti-DHBV capsid antiserum, and core-associated RNA was isolated. For comparison, total RNA was prepared from the same transfections. RNAs were separated by agarose gel electrophoresis, and hybridized with a DIG-labeled DNA probe specific for DHBV pgRNA. The position of a 3.5 kb marker RNA is indicated on the right.
