Figure 3. Cryo-EM structure of the Cbf1-nucleosome complex reveals specific interactions between the Cbf1 HLH domain and histones.
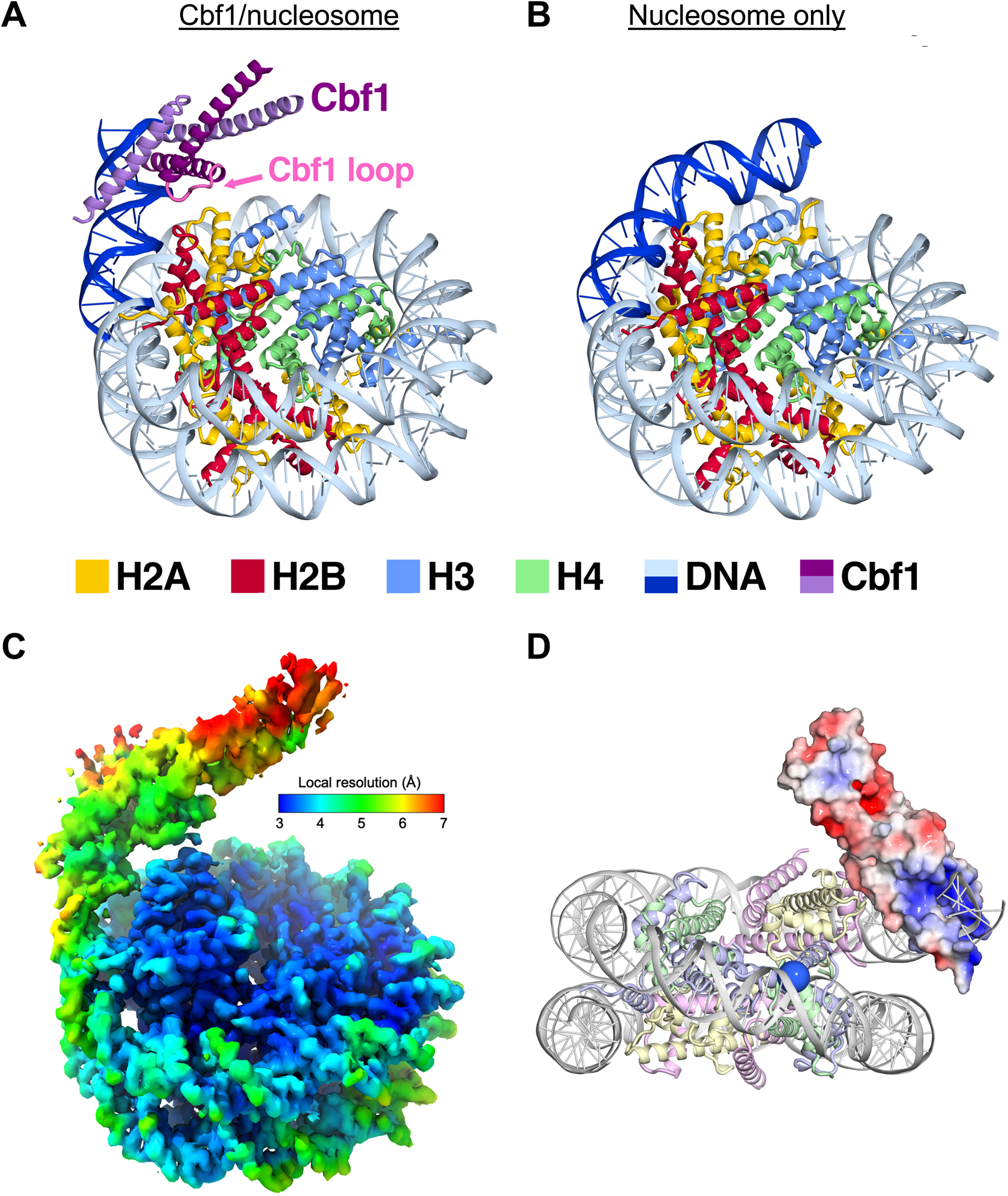
(A) Ribbon representation of Cbf1-nucleosome complex. The Cbf1 dimer is colored in light and dark purple. The unwrapped DNA is in dark blue, while the DNA in contact with the histone octamer is in sky blue. Histone H2A, H2B, H3 and H4 are colored in yellow, red, light blue and light green, respectively. (B) A ribbon representation of the fully wrapped nucleosome.40 The coloring is the same as in panel (A). (C) The 3.2-Å 3D reconstruction used for model building colored by local resolution. (D) Negatively charged patches of Cbf1 (red surfaces) may interact with positively charged histone tails. The APBS-calculated electrostatic86 potential was mapped from −5 to 5 kT/e. The view faces the nucleosome dyad. To indicate where the H3 N-terminal tail extends out, the Cα of the first modeled histone H3 residue, Pro43, is rendered as a blue sphere.
