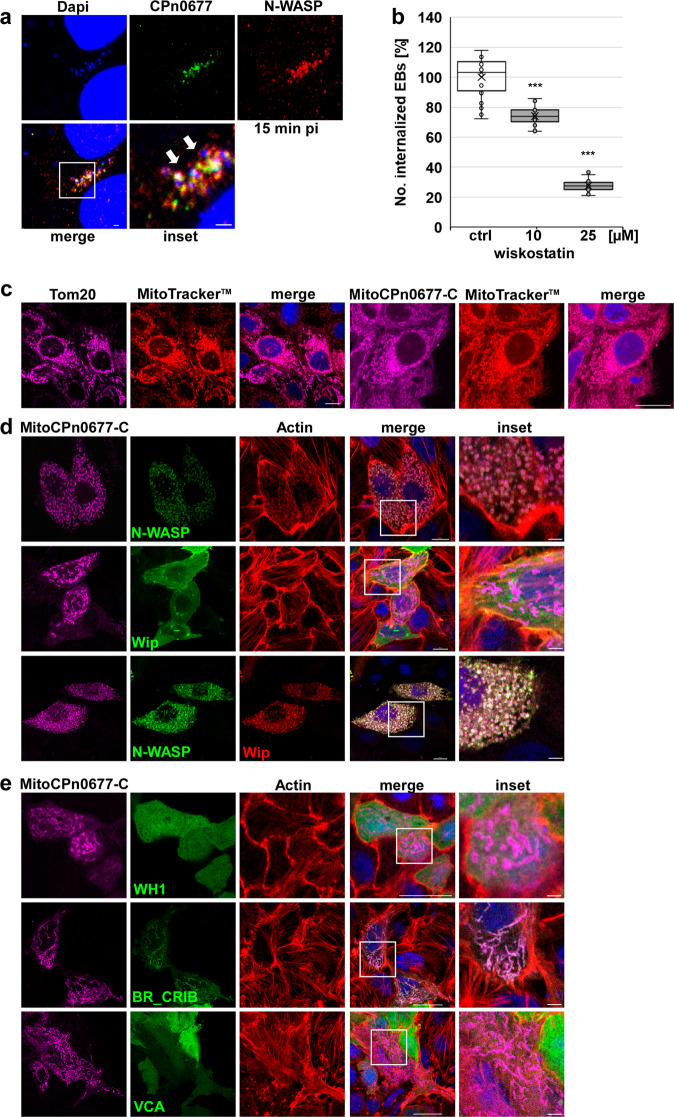
Fig. 3. CPn0677 recruits N-WASP to bacterial entry sites and activates it.
a Colocalization of N-WASP (stained with anti-N-WASP and anti-mouse Alexa594 antibodies) and CPn0677 (stained with anti-CPn0677 and anti-rat Alexa488 antibodies) at bacterial entry sites at 15 min pi. C. pneumoniae EBs were stained with DAPI. The inset shows region outlined by the white frame. White arrowheads show areas of colocalization. Bar = 10 µm, insets 1 = µm. b Quantification of uptake of EBs into HEp-2 cells pretreated for 5 min with either DMSO or wiskostatin (10 and 25 µM) and washed three times with PBS prior to infection. At 2 hpi cells were fixed, and external EBs were stained using an anti-LPS antibody in combination with anti-mouse Alexa488. All EBs were stained with DAPI. External and internalized EBs were quantified based on the examination of 40 visual fields. Data are represented as means ± SD (n = 4 biologically independent experiments). P value: ***≤0.001. c HEp-2 cells expressing either Tom20 or MitoCPn0677-C fused with SNAP were stained with MitoTracker™Red. DNA was visualized with DAPI. Bar = 10 µm. d, e Confocal images of the mitochondrion-targeted MitoCPn0677-C, co-expressed with the indicated N-WASP variants and the N-WASP interactor Wip. Insets show regions outlined by the white frames. d HEp-2 cells co-expressing MitoCPn0677-C fused to SNAP with wild-type GFP-N-WASP or GFP-Wip. e HEp-2 cells co-expressing MitoCPn0677-C and different N-WASP subdomains (depicted in Supplementary Fig. S2b) fused to GFP. Cells were fixed and F-actin was stained with rhodamine-phalloidin. DNA is visualized using DAPI. Bar = 10 µm, insets = 5 µm.