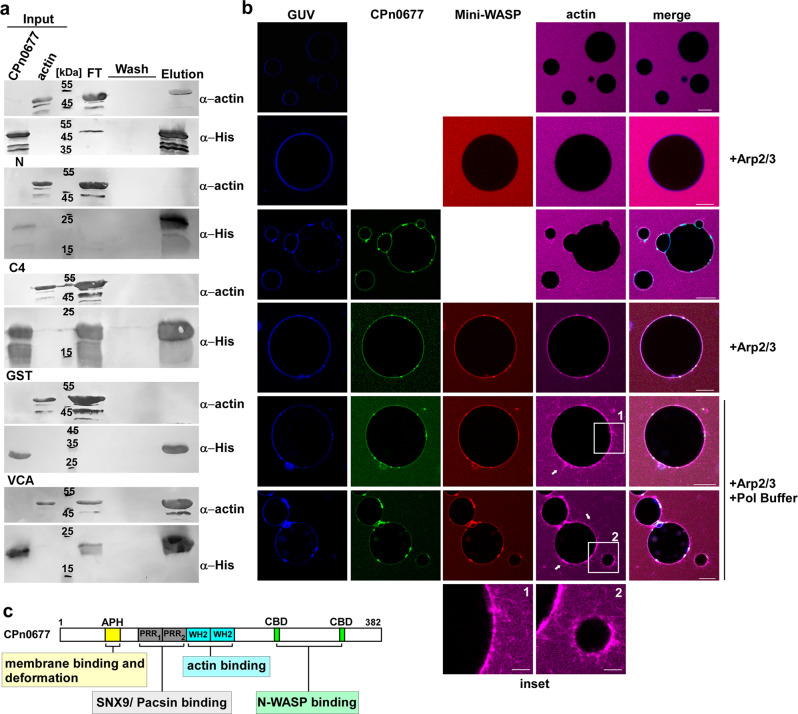
Fig. 4. G-actin-bound CPn0677 recruits and activates human N-WASP to polymerize actin filaments in PS-containing GUVs.
a Pulldown experiments using monomeric G-actin (100 µg) in combination with His-tagged CPn0677, CPn0677-N, or CPn0677-C4 (100 µg). The His-tagged VCA domain (N-WASP) and GST served as positive and negative controls, respectively. Input, flow through (FT), wash and elution samples obtained from His-pulldowns were fractionated by SDS/PAGE and probed with anti-actin and anti-His antibodies. b Confocal images of PS-containing GUVs labeled with Marina Blue™, and incubated and imaged for 10–15 min after addition of the various labeled and unlabeled proteins. The top two rows show GUVs that had been incubated with 3 µM G-actin Atto647 alone or in combination with 3 µM NHS-rhodamine-labeled mini-WASP and unlabeled Arp2/3 complex (100 nM). For next two rows 3 µM FITC-labeled CPn0677 was added to the mixture. In the last two last rows G-actin, CPn0677, Mini-WASP and Arp2/3 were added to the GUVs before actin polymerization was started by addition of 1 x actin polymerization buffer. Actin polymerization on the GUV membrane was imaged for 15 min. Bar = 10 µm. c Schematic representation of the multifactorial interactions of Cpn0677 with different, central endocytic host proteins analyzed in this report.