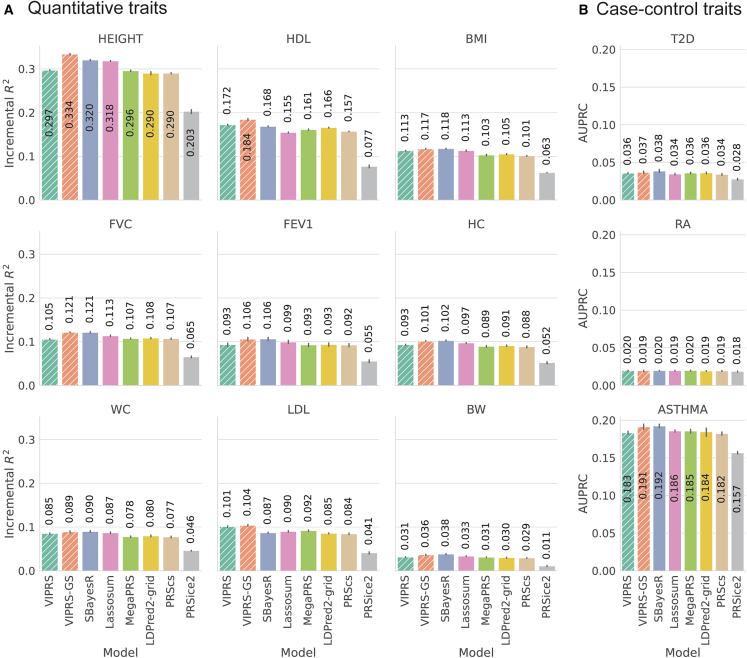
Figure 3.
Predictive performance of summary statistics-based PRS methods on real quantitative and case-control phenotypes in the UK Biobank
(A and B) The measured phenotypes were pre-processed and analyzed in a 5-fold cross-validation study design and the prediction metrics show the performance of each PRS method in predicting the phenotype in a held-out test set. Each panel shows the predictive performance, in terms of (A) incremental and (B) area under the precision recall curve (AUPRC), of various PRS methods when applied to a given phenotype. The bars show the mean of the prediction metrics across the five folds and the black lines show the corresponding standard errors. The quantitative phenotypes analyzed are standing height (HEIGHT), high-density lipoprotein (HDL), body mass index (BMI), forced vital capacity (FVC), forced expiratory volume in 1 s (FEV1), hip circumference (HC), waist circumference (WC), low-density lipoprotein (LDL), and birth weight (BW). The binary phenotypes analyzed are asthma (ASTHMA), type 2 diabetes (T2D), and rheumatoid arthritis (RA). The PRS methods shown are our proposed VIPRS and VIPRS-GS (using grid search to tune model hyperparameters) as well as six other baseline models: SBayesR, Lassosum, MegaPRS, LDPred2 (grid), PRScs, and PRSice2 (C+T). Dashed lines highlight the models contributed in this work.