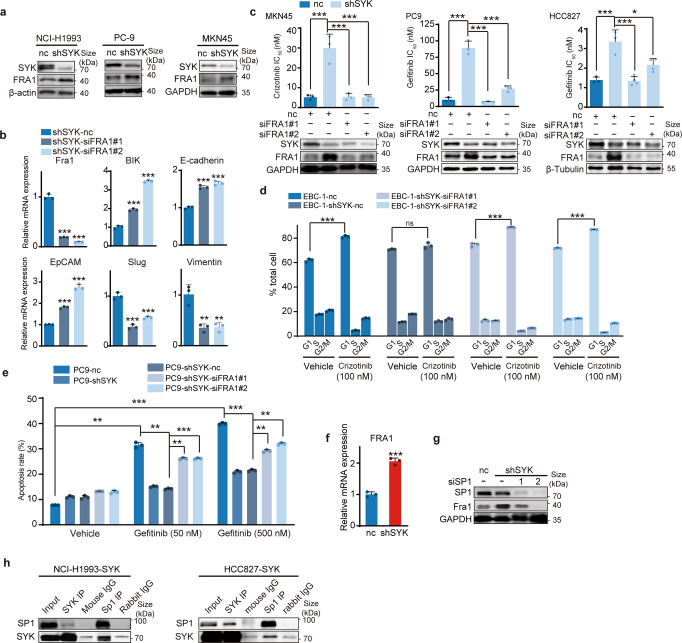
Fig. 2.
SYK interacts with Sp1, suppressing Sp1-induced FRA1 transcription and conferring sensitivity to kinase inhibitors. a Immunoblotting analysis of FRA1 in cell lines upon stable SYK knockdown. b qRT‒PCR analysis of the representative E/M classic markers in HCC827-shSYK cells upon transient transfection with FRA1 siRNA. c Change in drug sensitivity in the indicated MET-amplified or EGFR-mutant cells with stable SYK knockdown upon further siFRA1 transient transfection. d Change in the cell cycle arrest of EBC-1-shSYK cells upon siFRA1 transient transfection. e Change in the apoptosis rate of PC9-shSYK cells upon siFRA1 transient transfection. f qRT‒PCR analysis of FRA1 transcriptional levels upon stable SYK knockdown in the HCC827 cell line. g Immunoblot analysis of FRA1 in PC9-shSYK cells upon Sp1 transient transfection. h Whole-cell lysates (WCLs) of SYK ectopically overexpressing NCI-H1993 or HCC827 cells were immunoprecipitated with antibodies against SYK or Sp1. Rabbit IgG antibody and mouse IgG antibody were used as negative controls for immunoprecipitation, and WCLs and coimmunoprecipitation were detected by immunoblotting, as indicated. The data shown are representative results from two or three independent experiments. The data in b, c, d, e, f are presented as the mean ± SD ***p < 0.001, **p < 0.01 and *p < 0.05, using one-way ANOVA in b, c and e; using Student’s t test in d and f