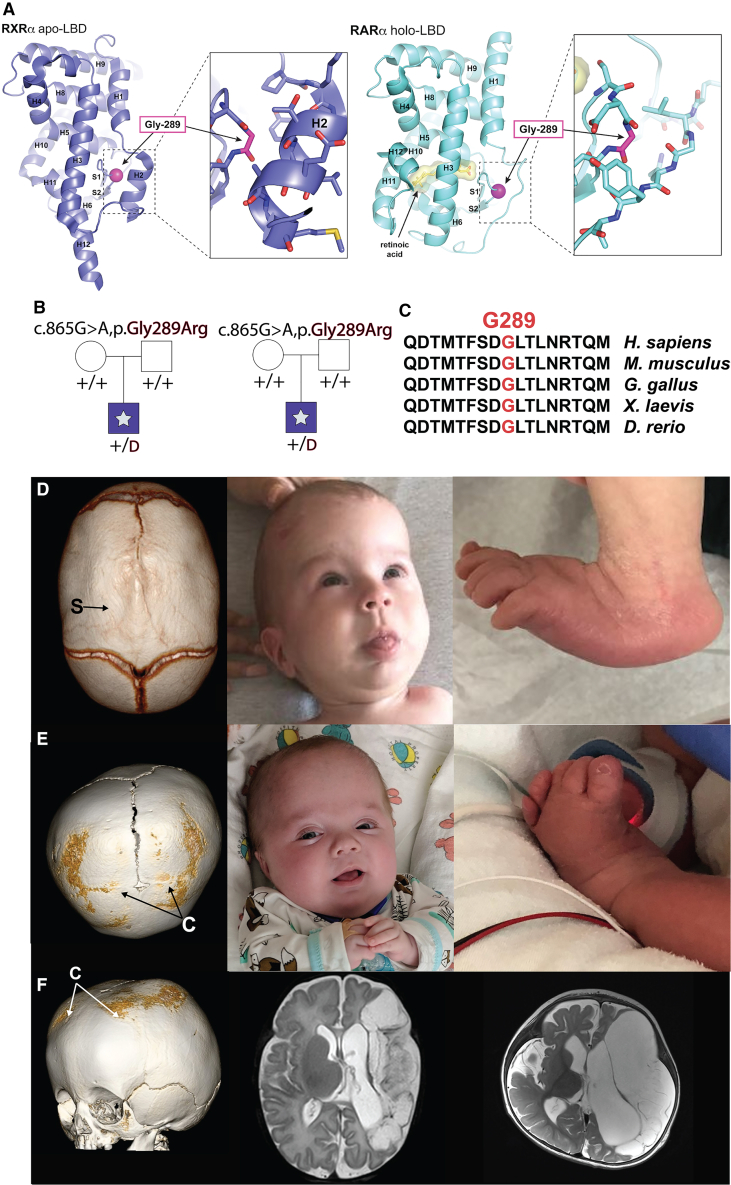
Figure 2.
A recurrent de novo p.Gly289Arg variant in RARA defines a craniosynostosis syndrome
(A) Left (purple): Ribbon diagram of the ligand binding domain of human retinoic acid receptor alpha. The diagram is modeled on the structure of the highly homologous retinoid receptor RXRα (PDB: 6HN643). Right (cyan): Ribbon diagram of the ligand binding domain of human retinoic acid receptor alpha (RARα) bound to all-trans retinoic acid (PDB: 3A9E44). The retinoic acid receptor alpha LBD, which is responsible for ligand binding, dimerization, and recruitment of coregulatory factors, adopts the typical helical sandwich fold that is characteristic of the large superfamily of nuclear receptors.45 It comprises twelve alpha-helices (H1–H12) and a beta turn (containing strands S1 and S2); retinoic acid ligands bind in a hydrophobic pocket involving helices H3, H5, and H11 and the beta turn. In response to ligand binding, the LBD undergoes a conformational change in helices H11, H12, H3, and H2. This conformational change leads to transcriptional activation. In both diagrams, alpha helices (H) and beta strands (S) are labeled according to the standard nomenclature for nuclear hormone receptor superfamily.45 Gly289, shown in magenta, is located within the beta turn loop connecting strands S1 and S2. Insets show the details of the sidechains of neighboring residues and demonstrate the surface inaccessibility of Gly289.
(B) Pedigrees of two families in which a recurrent de novo variant in RARA were detected. + represents a wild-type allele, and D represents the variant described above each pedigree.
(C) Protein sequence alignment of RARA, demonstrating evolutionary conservation of Gly289 and its flanking sequence across several recent orthologs.
(D) 3D CT scan demonstrating sagittal CS (S) in a proband, as well as associated head shape and rocker-bottom feet.
(E) CT scan demonstrating bilateral coronal CS (C), associated brachycephaly, and similar foot deformity present bilaterally.
(F) Frontal view of 3D CT reconstruction demonstrating bilateral coronal CS, and MRI images demonstrating sequelae of perinatal middle cerebral artery stroke.