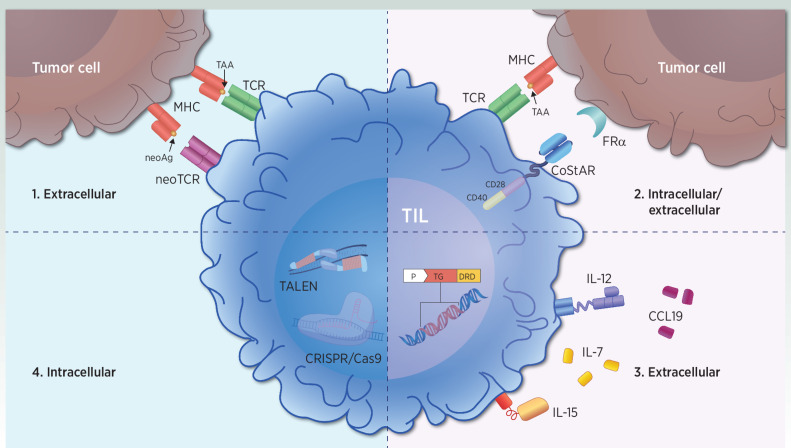
Figure 2.
Strategies to optimize T-cell activation in next-generation TIL. Immune-modulation strategies involve improvements in intracellular and extracellular signaling. Strategy 1. Extracellular T-cell activation occurs via TCR/neoTCR-mediated recognition of TAA or neoAg peptides. Novel therapeutic products select and enrich for pre-existing tumor antigen-specific T cells. Strategy 2. Intracellular and extracellular enhancements of T-cell activation and effector function occur through dual CD28 and CD40 intracellular signaling domain-mediated costimulation upon TCR-mediated antigen recognition. Strategy 3. Extracellular T-cell activation through the local delivery of immunomodulatory molecules such as IL7 and CCL19, as well as cell-anchored IL12, or drug-inducible membrane-bound IL15 expression. Strategy 4. Increasing T-cell fitness and reducing T-cell exhaustion with intracellular strategies such as PDCD-1 knockout with TALEN, and CT-1 knockout with CRISPR/Cas9. CCL, chemokine (C–C motif) ligand; FRα, folate receptor alpha; neoAg, neoantigens; TAA, tumor-associated antigens.