Figure EV2. Developmental and housekeeping promoters bind different sets of proteins and GTFs.
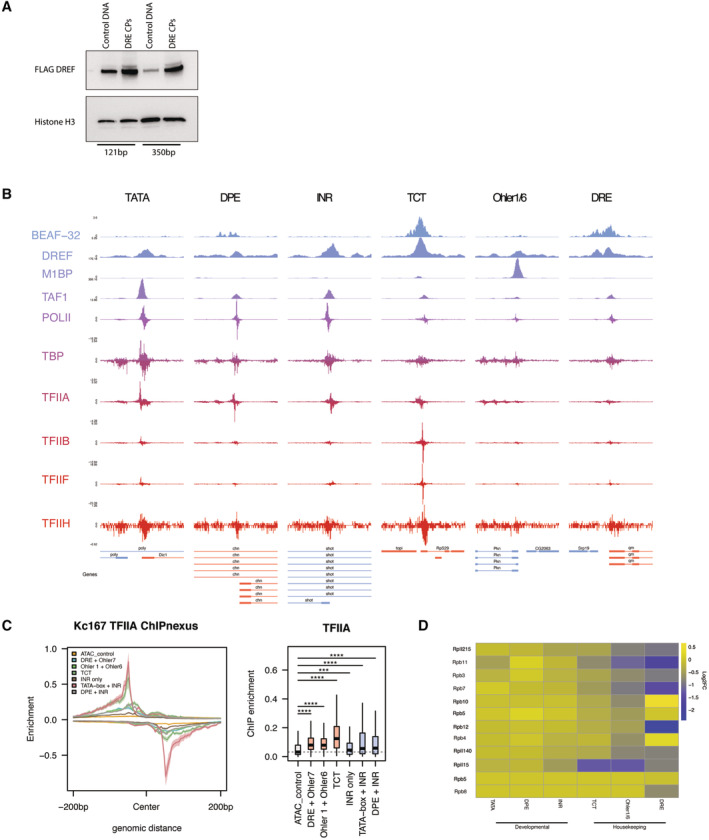
- Elution fractions from the DNA‐purification assay with a pool of 20,121 bp or a pool of 10,350 bp DRE promoters and length‐matched negative controls were performed with a nuclear extract expressing DREF‐AID‐3xFLAG tag and blotted for an anti‐FLAG antibody. Both promoter lengths are able to enrich for DREF binding.
- Representative browser tracks of published ChIP‐seq data of GTFs and promoter binding TFs (M1BP, DREF, BEAF‐32) on the 6 different tested promoter types in this study.
- Meta‐plot of TFIIA‐L ChIP‐seq data from panel E at the 6 different tested promoter types indicating TFIIA binds all active promoter types, although less strongly to housekeeping promoters and in a more dispersed fashion relative to the TSS (center). Box plot quantification of TFIIA ChIP‐seq data at /+ 200 bp around the TSS. Boxes represent the upper and lower quartiles, with the middle band at the median. The whiskers represent 1.5 times the interquartile range across two biological replicates, outliers not shown. (****P < 1e‐5, ***P < 1e‐3, **P < 1e‐2, *P < 5e‐2, N.S = not significant).
- Heat map of log2FC values of DNA affinity purification values for RNA polymerase II subunits across the six different promoter types tested.
