Figure 6. Housekeeping cofactor recruitment is sufficient to recapitulate dispersed transcription initiation patterns.
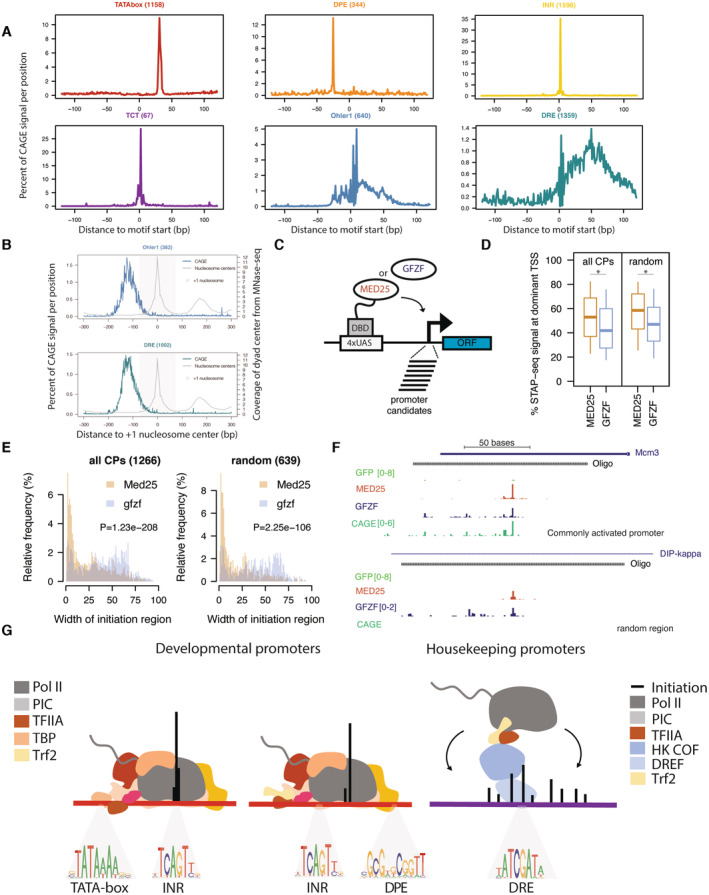
- Distribution of CAGE signal from mixed D. mel embryos (0‐24 h) centered on the location of promoter DNA motif sequence set at position 0 across the 6 main promoter types investigated in this study.
- Relative CAGE signal per position on all active promoters containing either Ohler 1 (top) or DRE (bottom) motif, aligned to the +1 nucleosome center (point of highest coverage of MNase fragment centers in +1 to +200 bp window relative to TSS).
- Scheme of cofactor recruitment STAP‐seq testing MED25 or GFZF Gal4 DNA‐binding domain fusions recruited to a library of candidate promoter fragments.
- Box plot of the percent of STAP‐seq signal (i.e., percent of initiation) originating at the dominant TSS at core promoters (CPs; N = 1,266) and random regions (N = 639) that are activated to similar extent by both GFZF and MED25 recruitment. Cofactor recruitment STAP‐seq data from (Haberle et al, 2019), three independent biological replicates merged. *P ≤ 0.01; Wilcoxon rank‐sum test.
- Histogram representing the distribution of the width of the initiation region (i.e., part of the oligo covered by STAP‐seq signal) for CPs (N = 1,266) and random regions (N = 639) upon recruitment of either MED25 or GFZF. P‐values: Wilcoxon rank‐sum test.
- Cofactor recruitment STAP‐seq tracks of GFP, MED25 and GFZF recruitment for examples of a core promoter and a random region that are activated by both cofactors. Endogenous initiation pattern in S2 cells (CAGE) is shown at the bottom.
- Scheme of Pol II PIC recruitment to the two types of developmental promoters (TATA‐box and non‐TATA‐box‐containing DPE and INR motifs), which occurs through direct engagement between the transcription machinery and developmental promoter sequence motifs, resulting in narrow initiation patterns, whereas housekeeping promoters recruit Pol II through housekeeping DNA‐binding proteins and intermediary cofactors that interact with TFIIA and Trf2, resulting in dispersed initiation.
