Figure 5. DAB operons are widespread among prokaryotes.
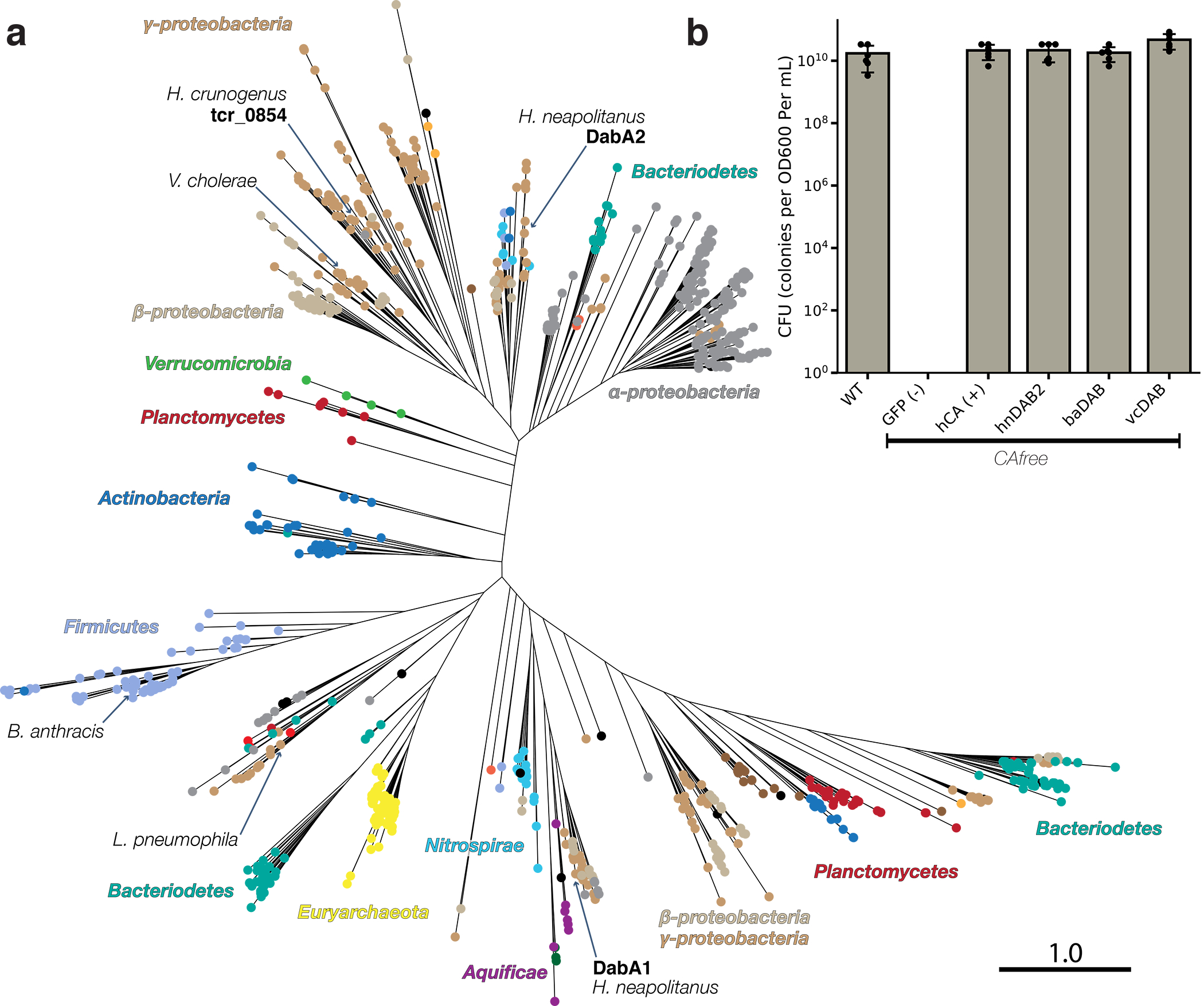
a. Approximate maximum likelihood phylogenetic tree of 878 DabA homologs associated with PF10070.9 (Methods). DabA homologs are found in > 15 prokaryotic clades, including archaea. Hnea DabA1 and DabA2 represent two different groupings that are commonly found in proteobacteria. Inspecting the tree reveals several likely incidents of horizontal transfer, e.g. between Proteobacteria and Firmicutes, Nitrospirae and Actinobacteria. Moreover, the genomes of several known pathogens contain a high-confidence DabA homolog, including B. anthracis, V. cholerae, and L. pneumophila. Detailed annotations are given in Supplemental Figure 9. Scale bar indicates one substitution per site. Sequences used to generate the tree can be found in Supplemental File 5. b. Functional DABs are found in human pathogens. Colony forming units per OD600 per ml were measured on LB plates with induction in air. DAB operons from B. anthracis (baDAB) and V. cholerae (vcDAB) rescued growth of CAfree cells. The Hnea operon DAB2 is abbreviated as hnDAB2. Bars represent means. Error bars represent the standard deviation of 6 technical replicate platings. Consistent results were achieved in biologically independent platings of baDAB and vcDAB.
