Figure 1.
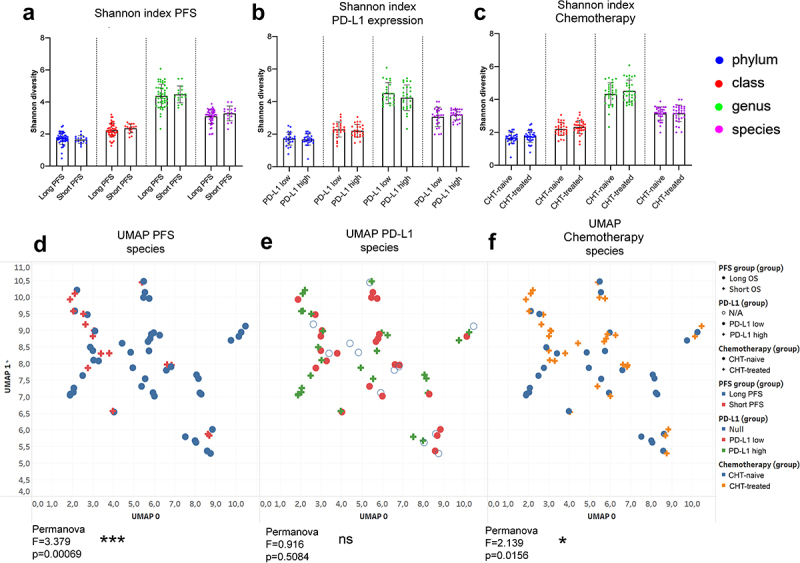
Alpha diversity and composition of bacterial communities (beta diversity). Shannon diversity index was calculated at phylum, class, genus and species taxonomy level according to long vs short PFS (cutoff 6 months), PD-L1 expression (≥50% high, <50% low) and front-line chemotherapy (CHT)-treatment prior to ICI. There was no significant difference in Shannon diversity index regarding PFS (A), PD-L1 expression (B) and CHT-treatment (C) using either taxonomic level. Diversity (Shannon and Simpson) indices and p-values for all alpha-diversity comparisons are listed in STable 3. Ordination plot using UMAP was generated from normalized, CLR-transformed bacterial abundances in the same comparisons. Permanova analysis was used to assess significant differences between the composition of bacterial communities. There was a significant difference between long- vs short PFS patients (F = 3.379, p = 0.0006, D) and between CHT-treated vs CHT-naive patients (F = 2.139, p = 0.0156, F), whereas no significant difference was detected between PD-L1 high vs PD-L1 low patients (F = 0.916, p = 0.0156, D) regarding the composition of bacterial species. Metric data are shown as mean and corresponding standard deviation (SD). Statistical significance *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01, ***P<.001. N/A: data not available.
