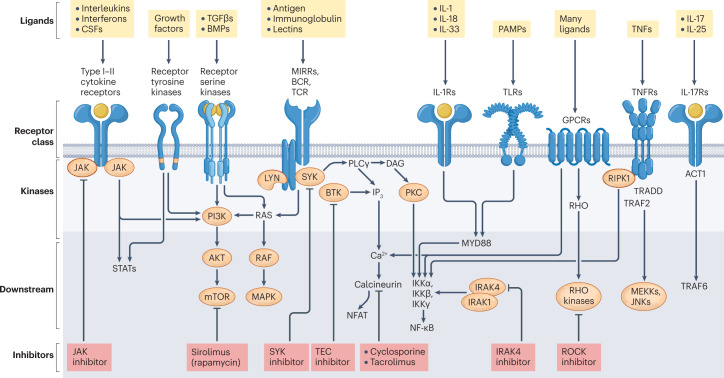
Fig. 1. Major kinase classes and immunoreceptor signalling.
Key immune receptors expressed by T cells, B cells and innate immune cells include different classes of cytokine receptors and multichain immune recognition receptors. Only a subset of downstream pathways are shown, which are relevant to the inhibitors discussed in this Review. The prominent kinases involved in immune receptor signalling include: receptor tyrosine kinases, receptor serine kinases, non-receptor tyrosine kinases such as the Janus kinases (JAKs) and the SRC (such as LYN), SYK and TEC (such as BTK) families of tyrosine kinases, as well as the larger group of downstream serine–threonine kinases. These are represented here with ligands, receptor classes, kinases and key downstream signalling cascades. BCR, B cell receptor; BMP, bone morphogenetic protein; BTK, Bruton’s tyrosine kinase; CSF, colony-stimulating factor; DAG, diacylglycerol; GPCR, G-protein-coupled receptor; IKKα, inhibitor of nuclear factor-κB kinase subunit-α; IKKβ, inhibitor of nuclear factor-κB kinase subunit-β; IKKγ, inhibitor of nuclear factor-κB kinase subunit-γ; IRAK, IL-1 receptor-associated kinase; JNK, JUN N-terminal kinase; MAPK, mitogen-activated protein kinase; MEKK, mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase; MIRR, multichain immune recognition receptor; mTOR, mammalian target of rapamycin; MYD88, myeloid differentiation primary response 88; NFAT, nuclear factor of activated T cells; NF-κB, nuclear factor-κB; PAMP, pathogen-associated molecular pattern; PI3K, phosphoinositide 3-kinase; PKC, protein kinase C; PLCγ, phospholipase Cγ; RIP, receptor-interacting serine–threonine protein kinase; ROCK, RHO-associated protein kinase; STAT, signal transducer and activator of transcription; SYK, spleen tyrosine kinase; TCR, T cell receptor; TGFβ, transforming growth factor-β; TLR, Toll-like receptor; TNF, tumour necrosis factor; TNFR, tumour necrosis factor receptor; TRADD, tumour necrosis factor receptor type 1-associated death domain; TRAF, TNFR-associated factor.