Extended Data Fig. 3. ΔyngC sensitizes B. subtilis to reduced levels of UndP synthesis.
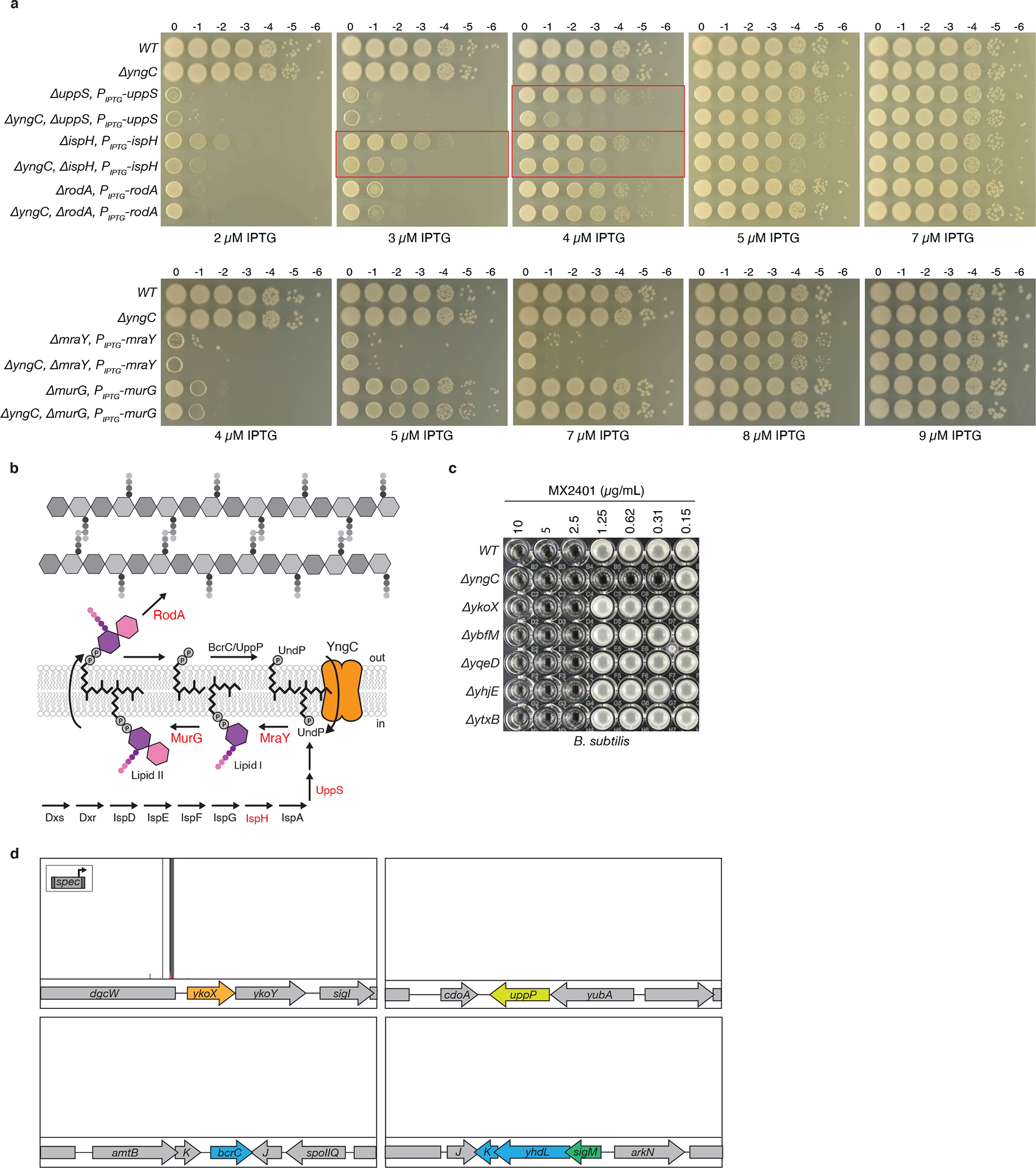
(a) Spot-dilutions of the indicated B. subtilis strains with IPTG-regulated alleles on LB agar supplemented with the indicated concentrations of IPTG. Strains with reduced levels of IspH or UppS are sensitive to the absence of yngC. Relevant comparisons are boxed in red. Strains with reduced levels of RodA, MurG or MraY grow similarly in the presence or absence of yngC. (b) Schematic of the UndP synthesis pathway illustrating the two sources of UndP for lipid II biogenesis: de novo synthesis and recycling. Enzymes shown in red were expressed at reduced levels in the assays in (a). (c) Minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) of MX2401 in the indicated B. subtilis strains, each lacks one of the six DedA paralogs. (d) The B. subtilis ΔyngC mutant was mutagenized with a transposon carrying a strong outward facing Ppen promoter (insert). The library was plated on LB agar supplemented with 0.3 μg/mL MX2401 to select for mutants that provide resistance. Transposon insertion profiles at the indicated B. subtilis genomic regions are shown. Each vertical line indicates an insertion site; its height reflects the number of sequencing reads at this position (maximum height ≥5000). The average number of reads was >40,000. The majority of insertions mapped upstream of the ykoX gene in an orientation that would increase its transcription. Transposon insertions were not enriched upstream of bcrC or uppP that encode UndPP phosphatases, suggesting that these proteins do not have UndP transport activity, as was proposed previously3,38. Unlike the Tn-seq screen in a wild-type (yngC+) background, in the ΔyngC mutant, transposon insertions were not enriched in the genes (yhdL and yhdK) encoding the anti-σM factors, consistent with the model that their inactivation provides increased MX2401 resistance by increasing σM-dependent transcription of yngC.
