Figure 2.
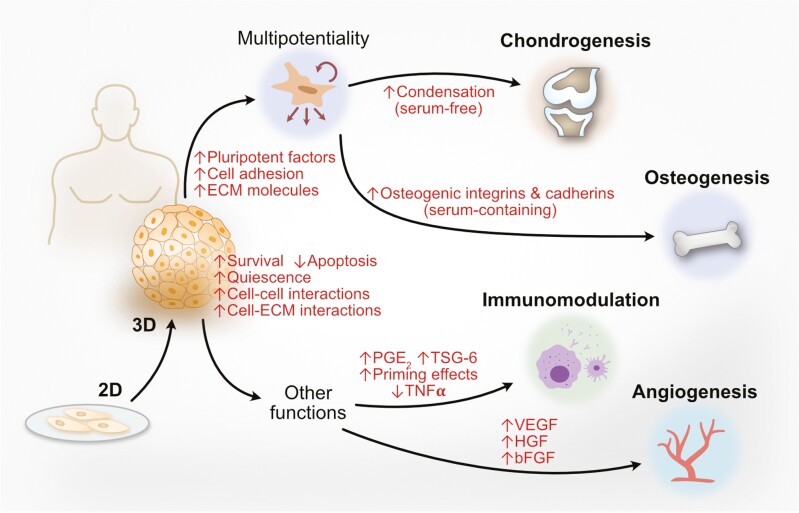
3-Dimensional (3D) multicellular spheroid culture of human mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) induce profound biological changes. Compared to 2D monolayer-cultured cells, 3D spheroid MSCs demonstrate improved cell viability/survival, decreased apoptosis, and increased cellular quiescence. Cell-cell and cell-extracellular matrix (ECM) interactions are increased as well. In terms of multilineage/multipotential differentiation capacity, MSC chondrogenesis requires 3D serum-free conditions to increase condensation, whereas 3D MSC spheroid culture under typical serum-containing conditions increase pluripotency factor expression as well cell adhesion and ECM proteins, especially for osteogenesis. Immunomodulation and angiogenic/wound healing functions are improved as well in 3D MSC spheroids, largely through the increased expression of many paracrine factors. PGE2, prostaglandin E2; TSG6, tumor necrosis factor-stimulated gene 6; TNFα, tumor necrosis factor-α; VEGF, vascular endothelial growth factor; HGF, hepatocyte growth factor; bFGF, basic fibroblast growth factor.