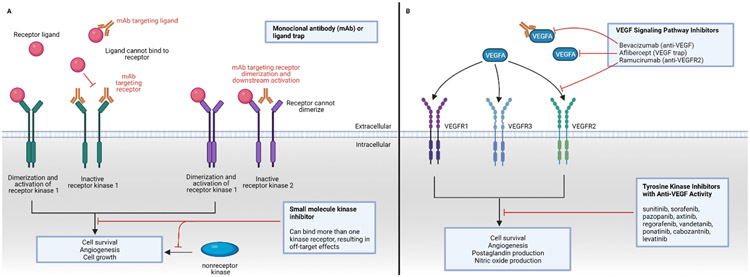
Figure 1:
Targeting kinases and VEGFR in the treatment of cancer. Panel A: Kinase inhibition can be achieved through targeting the kinase receptor ligand or kinase receptor, usually through binding of a monoclonal antibody (mAb) that is given as an intravenous infusion. Small-molecule kinase inhibitors, taken orally, work intracellularly and may bind more than one kinase. Panel B: VEGF-targeted therapies include a monoclonal antibody and ligand trap against circulating VEGFA, a monoclonal antibody against VEGF receptor 2 (VEGFR2), and multitargeted tyrosine kinase inhibitors with anti-VEGF activity.