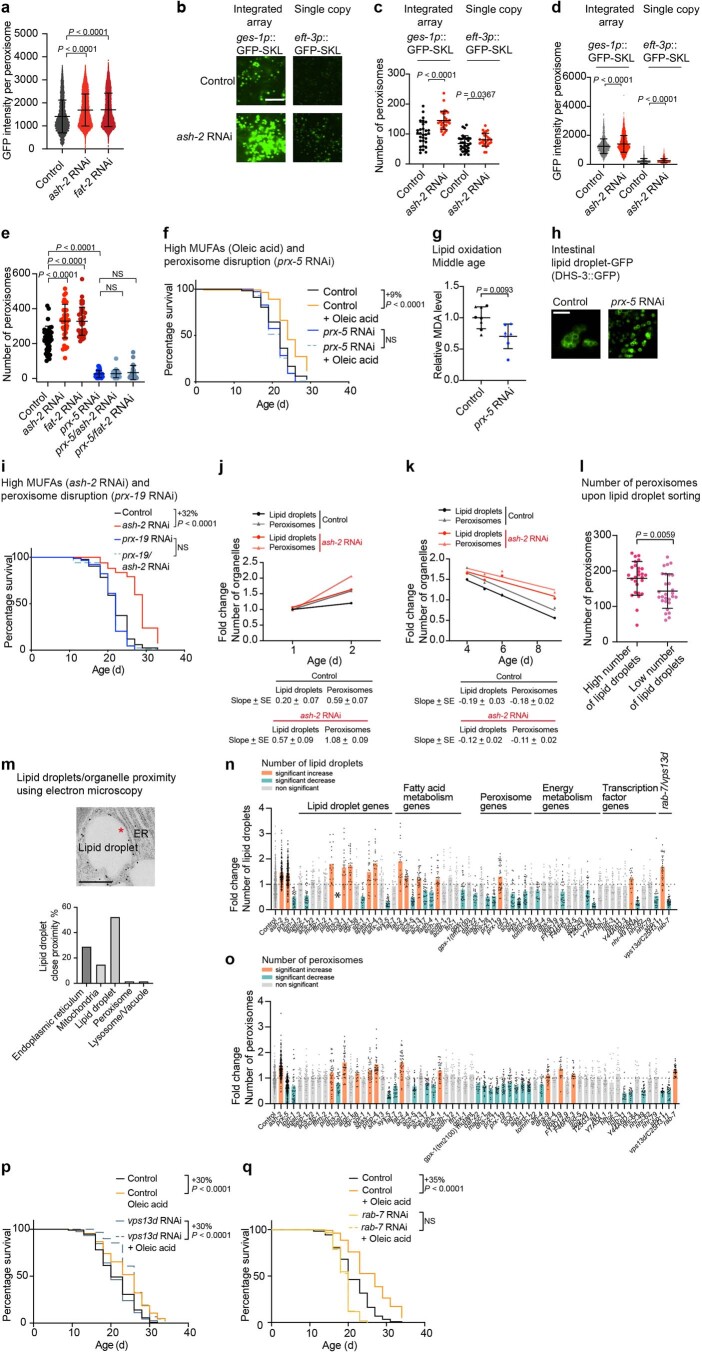
Extended Data Fig. 5. Interventions that regulate the number of peroxisomes and lipid droplets.
a, Quantification of intestinal peroxisome-localized GFP intensity, measured by fluorescence, in ges-1p::GFP–SKL worms following MUFA accumulation; n = 6,061, 13,446 and 10,598 peroxisomes in ≥35 worms treated with control, ash-2 and fat-2 RNAi, respectively. Data are the mean ± s.d. Each dot represents the GFP intensity of one peroxisome. P values: two-tailed Mann–Whitney test. Peroxisomes shown in Fig. 7c. b–d, Intestinal peroxisomes, assessed by fluorescence, in worms expressing an integrated array of ges-1p::GFP–SKL or a single copy knock-in of a peroxisome-localized GFP (GFP–SKL) driven by the ubiquitous eft-3 promoter (eft-3p::GFP–SKL) following ash-2 depletion. b, Zoomed-in images of the intestine. Scale bar, 5 µm. c, Quantification of peroxisome number; n = 30, 29, 32 and 27 ges-1p::GFP–SKL worms treated with control and ash-2 RNAi, and eft-3p::GFP-SKL worms treated with control and ash-2 RNAi, respectively. Data are the mean ± s.d. Each dot represents the peroxisome number in a 13 × 13 µm2 area in the intestine of an individual worm. P values: two-tailed Mann–Whitney test. d, Quantification of peroxisome-localized GFP intensity; n = 1,922, 2,814, 1,537 and 1,553 peroxisomes in ≥22 ges-1p::GFP–SKL worms treated with control and ash-2 RNAi, and eft-3p::GFP–SKL worms treated with control and ash-2 RNAi, respectively. Analysis in a. e, Quantification of intestinal peroxisomes, measured by fluorescence, in ges-1p::GFP–SKL worms following prx-5 depletion and MUFA accumulation; n = 39, 38, 40, 33, 26 and 22 worms treated with control, ash-2, fat-2, prx-5, ash-2 + prx-5, and fat-2 + prx-5 RNAi, respectively. Data are the mean ± s.d. Each dot represents the peroxisome number in a 26 × 26 µm2 area in the intestine of an individual worm. P values: two-tailed Mann–Whitney test. f, prx-5 is necessary for longevity following oleic acid supplementation; n ≥ 120 worms for each condition. Percentages of median lifespan extension and P values are indicated. P values: log-rank Mantel–Cox test. g, Lipid oxidation quantified via MDA levels following prx-5 depletion; n = 8 and 7 samples from worms treated with control and prx-5 RNAi, respectively. Normalized to the control condition. Data are the mean ± s.d. of two independent experiments. Each dot represents a biological replicate. Each shape represents an independent experiment. P values: two-tailed Mann–Whitney test. h, Intestinal lipid droplet number, assessed by fluorescence, in dhs-3p::dhs-3::GFP worms following prx-5 depletion. Zoomed-in images of the intestine. Scale bar, 5 µm. Lipid droplet number quantified in n. i, prx-19 is necessary for longevity following ash-2 depletion; n ≥ 95 worms for each condition. Analysis as in f. j,k, Intestinal lipid droplet and peroxisome number, measured by fluorescence, in dhs-3p::dhs-3::GFP; vha-6p::mRFP–SKL worms during aging and following ash-2 depletion; n ≥ 23 worms. Data are the mean ± s.d. Each dot represents the mean organelle number of all worms imaged for this condition normalized to young control (adult day 1) worms. Organelle number increases at younger ages (j) and organelle number decreases at older ages (k). Linear regression fit. l, Intestinal peroxisomes, measured by fluorescence, in dhs-3p::dhs-3::GFP; vha-6p::mRFP–SKL worms after sorting based on lipid droplet number using a BioSorter; n = 27 and 28 worms sorted based on high and low lipid droplet number, respectively. Analysis as in e. m, Lipid droplets assessed by immunogold labeling (against GFP) using transmission electron microscopy in dhs-3p::dhs-3::GFP worms. The asterisk indicates close proximity/contact between a lipid droplet and the endoplasmic reticulum (top). Scale bar, 500 nm. Quantification of lipid droplet contact/close proximity with other organelles as a percentage (bottom). n, Intestinal lipid droplets, measured by fluorescence, in dhs-3p::dhs-3::GFP; vha-6p::mRFP–SKL transgenic worms following treatment with 62 different RNAis; n = 19–423 worms. Data are the mean ± s.d. Each dot represents the organelle number in a 26 × 26 µm2 area in the intestine of an individual worm normalized to control worms. Orange, significant increase in organelle number. Turquoise, significant decrease in organelle number. P values: two-tailed Wilcoxon test with Benjamini–Hochberg test for multiple hypothesis correction. Conditions are colored if the adjusted P < 0.05. *dhs-3 RNAi abolishes the GFP signal of the lipid droplet DHS-3::GFP reporter. o, Quantification of intestinal peroxisome measured by fluorescence in dhs-3p::dhs-3::GFP; vha-6p::mRFP–SKL transgenic worms. Quantification of peroxisome number in worms treated as in n; n = 18–286 worms for each condition. Analysis as in n. p, vps13d depletion does not reduce longevity following oleic acid supplementation; n ≥ 99 for each condition. Analysis as in f. q, rab-7 depletion reduces longevity following oleic acid supplementation; n ≥ 120 for each condition. Analysis as in f. a,e, Representative of three independent experiments. c,d,f,i–m,p,q, Representative of two independent experiments. Source numerical data of all experiments, replicates, exact n values and statistics as well as Cox proportional hazard interaction values are provided.