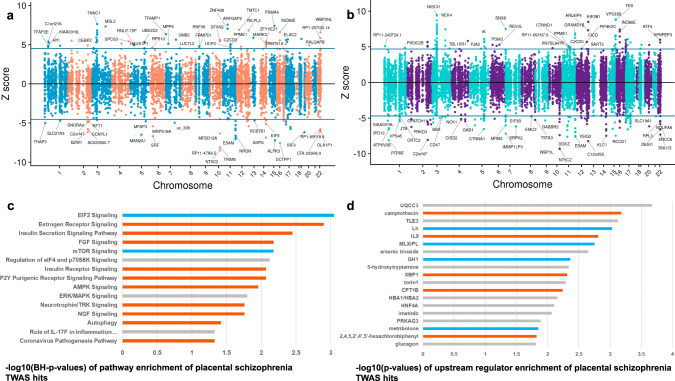
Fig. 1. Schizophrenia TWAS in placenta.
Results from TWAS prioritize genes (a) and transcripts (b) whose cis-regulated expression in placenta (N = 146 for the gene-level TWAS; N = 147 for the transcript-level TWAS) is associated with disease. Plots show conditionally-independent TWAS prioritized genes (a) and transcripts (b). The sign of TWAS z-scores (y-axis) indicates predicted direction of effect. Genes with predicted expression significantly up- or down-regulated in placenta are respectively above and below the horizontal lines corresponding to the TWAS level of significance after Bonferroni correction for multiple comparisons. 100 genes and 235 transcripts are significantly associated with schizophrenia (corresponding to 262 unique genes). Pathway (c, top 12 and selected) and upstream regulators (d, selected) enriched for the schizophrenia risk genes identified with the TWAS (N of genes = 262): bars depict negative logarithm of the P values (orange bars: activation, turquoise: inhibition, gray: absence of predicted directionality; negative logarithm of Benjamini–Hochberg corrected p-values are shown in (c), of uncorrected p value in (d) from right-tailed Fisher’s Exact Test.