Figure 7.
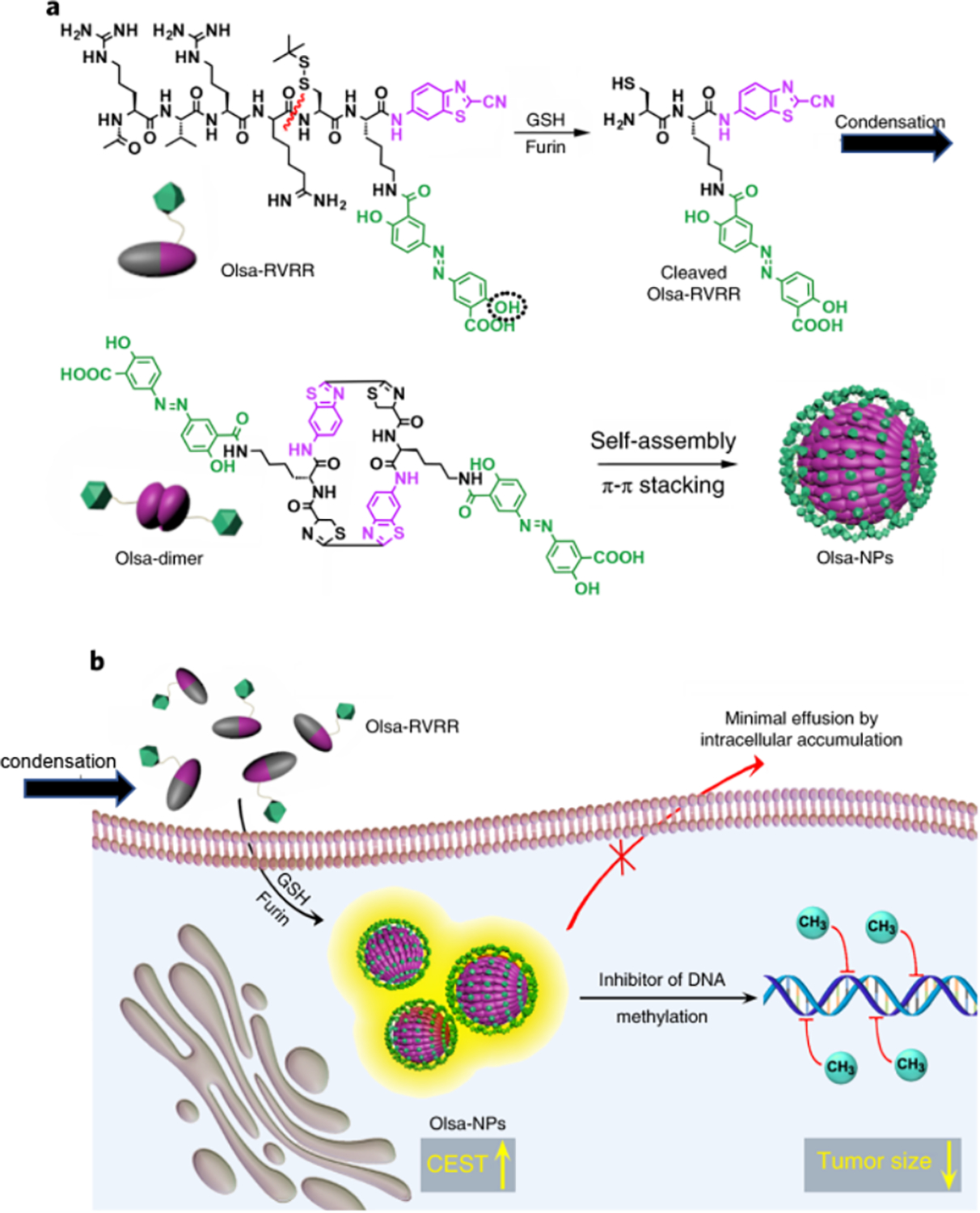
(a) Self-assembly of Olsa-RVRR into Olsa-NPs through a series of steps. Red line indicates the site of furin cleavage, and the circled hydroxyl group indicates the exchangeable hydroxyl proton that provides OlsaCEST signal at 9.8 ppm from the water frequency. (b) After Olsa-RVRR enters the cytoplasm of high furin-expressing cells (HCT116 cells in this study), it undergoes reduction by GSH and cleavage of the peptide by furin near the Golgi complex where cleaved Olsa-RVRR is generated. Amphiphilic oligomers (mostly dimers) are then formed from the click reaction between two cleaved Olsa-RVRR molecules, followed by self-assembly into Olsa-NPs as a result of intermolecular π–π stacking. The intracellular accumulation of Olsa-NPs then serves as a reservoir of Olsa molecule-enhancing CEST contrast and inhibiting DNA methylation for tumor therapy. Reprinted with permission from [40].
