Figure 2.
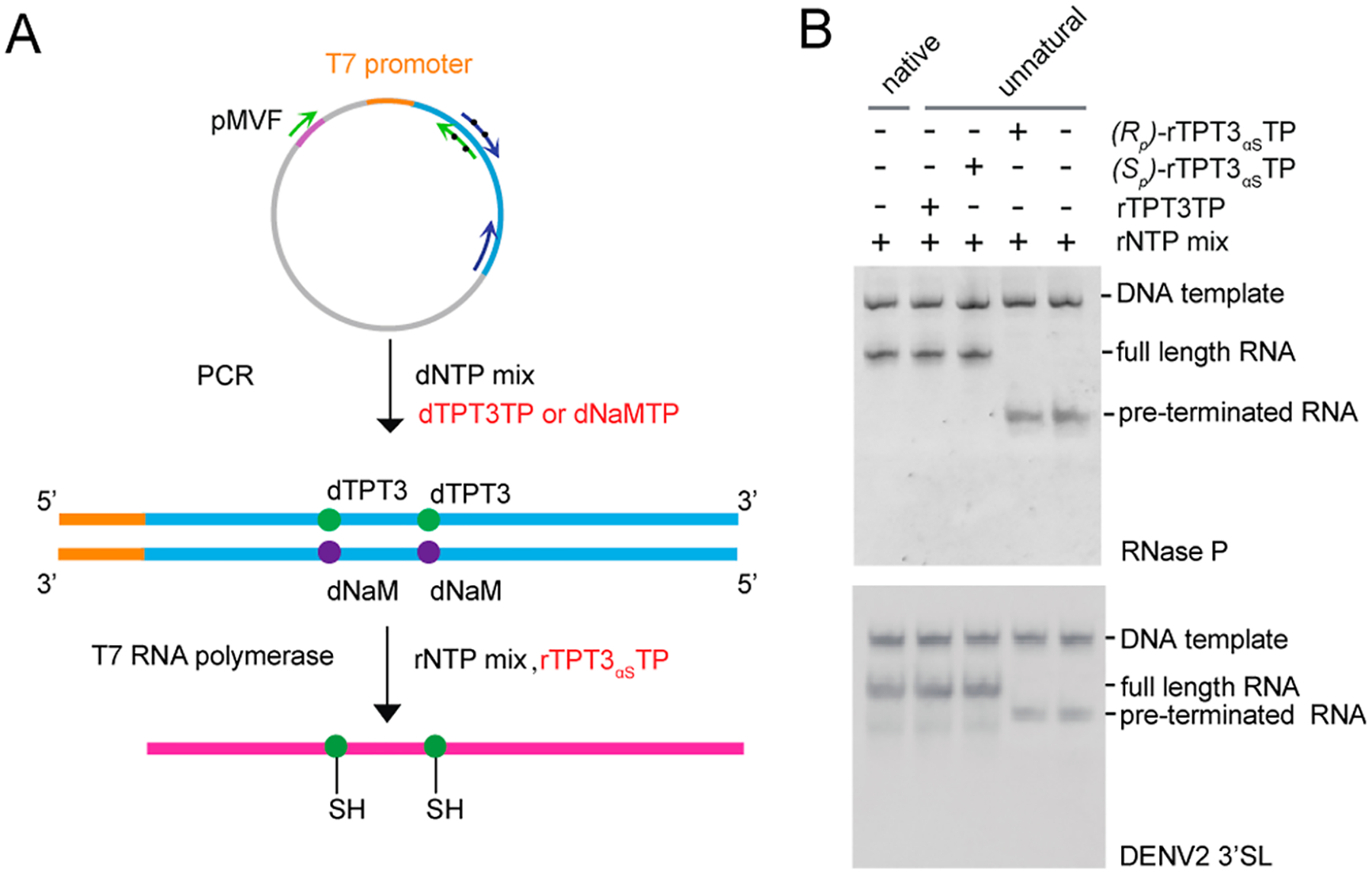
Site-specific PS modification of large RNAs by transcription of an expanded genetic alphabet containing TPT3-NaM UBP. (A) General procedure for site-specific PS modification of RNA. The double-stranded DNA template containing one or two dNaM modifications at the template strand can be prepared by PCR using a plasmid DNA template and single-stranded UBP-modified DNA primers. PSs can be site-specifically introduced into RNAs by IVT using an rNTP mix supplemented with (Sp)-rTPT3αSTP. (B) Native PAGE analysis of IVT of native or UBP-modified DNA templates encoding (upper) RNase P and (lower) DENV2 3′SL using Sp and Rp diastereomers of rTPT3αSTP. T7 RNAP only accepts (Sp)-rTPT3αSTP as a substrate for IVT. Transcription of native DNA template using rNTP mix results in one single band. rTPT3 or (Sp)-rTPT3αS can be efficiently incorporated into RNase P RNA and 3′SL by an IVT reaction catalyzed by T7 RNAP. If no rTPT3TP or only (Rp)-rTPT3αSTP is added to the IVT reaction, no full-length RNAs but only short abortive transcripts are observed.
