Figure 1.
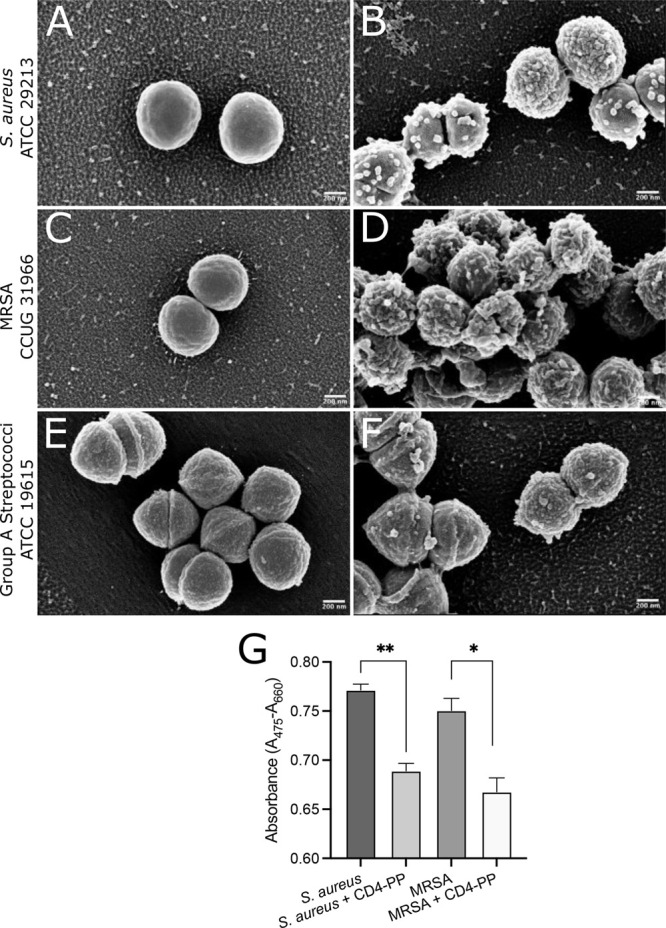
CD4-PP induces membrane damage and decreases bacterial metabolic activity. Representative scanning electron microscopy images of (A,B) S. aureus ATCC 29213, (C,D) MRSA CCUG 31966, and (E,F) group A streptococci (GAS) ATCC 19615 with or without CD4-PP treatment. Blebs are seen on the surface of all CD4-PP-treated bacteria compared with controls. (G) Metabolic activity expressed as conversion of tetrazolium salt XTT to a colored formazan derivative by S. aureus (n = 3) and MRSA (n = 3) with or without CD4-PP treatment (**p < 0.01, *p < 0.05, unpaired t test).
