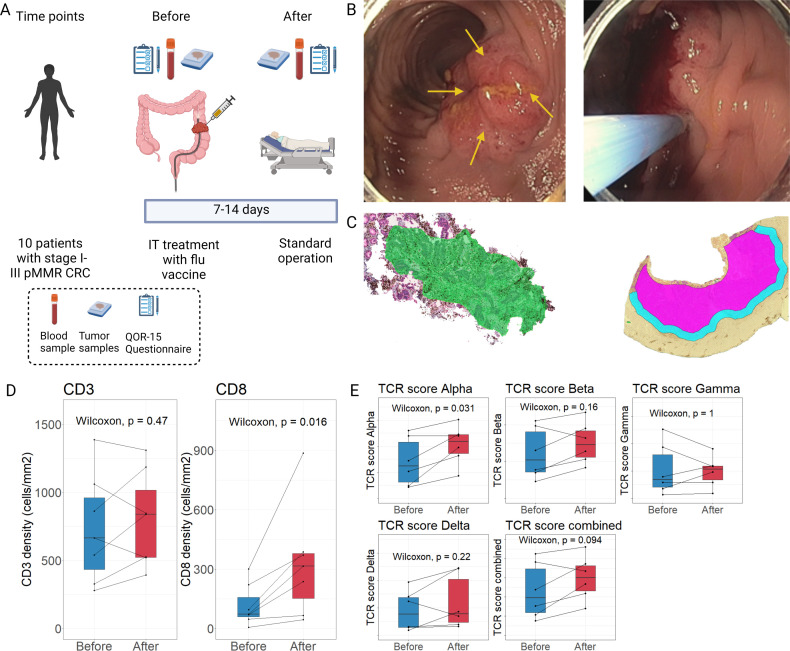
Figure 1.
Neoadjuvant intratumoral influenza vaccine treatment increases CD8+T-cell infiltration and TCR alpha chain diversity. (A) Overview of the study design and sample time points. At each time point, blood and tumor samples were taken and a QoR-15 questionnaire was filled. (B) Representative pictures showing the quadrant visualization (yellow arrows, left picture) and intratumoral (IT) injection of the influenza vaccine (right picture). (C) Representative tumor tissue slides from immunohistochemistry (IHC) staining with anti-CD3/cytokeratin for digital analysis of T-cell infiltration. Tumor slides with IHC staining of anti-CD8/cytokeratin are not shown. Left picture shows a representative sample from before vaccination. Right picture shows a sample after the vaccination with the central tumor (pink) and invasive margins (light blue). (D) Comparison of the IHC staining density of CD3+ and CD8+ T cells before (green area) and after vaccination (pink area) samples (n=7). (E) Comparison of alpha, beta, gamma, and delta variable chains, and combined variable chain score between time points (n=6). (D, E) CD3+ and CD8+ T-cell densities and normalized expression of TCR variable chain expression depicted as boxplot showing median, upper and lower quartiles. Whiskers extend into a max of 1.5 times the IQR. CRC, colorectal cancer; pMMR, proficient mismatch repair; QoR-15, quality of recovery 15 questionnaire; TCR, T-cell receptor.