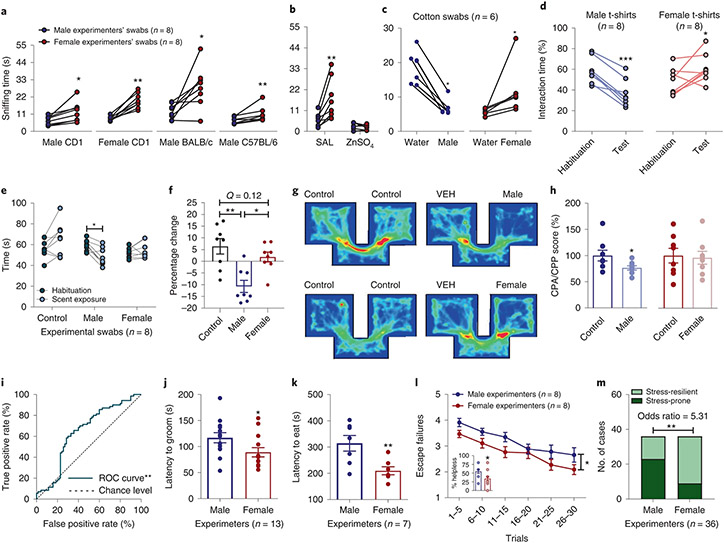
Fig. 1 ∣. Mice manifest differential behavioral responses following exposure to male and female experimenter scent.
a,b, Interaction time of experimentally naïve CD1 (P = 0.010 males, P = 0.008 females), BALB/cAnNCrl (P = 0.016), C57BL/6J (P = 0.008) (n = 8 experimenters per strain per sex; n = 32 mice per strain; two-sided paired t-test or Wilcoxon matched-pairs signed-rank test) (a) and anosmic CD1 mice with male versus female experimenter skin swabs (n = 8 experimenters per treatment group per sex; n = 16 mice per treatment group; two-sided Wilcoxon matched-pairs signed-rank test; SAL P = 0.008, ZnSO4 P = 0.945) (b). c,d, Time spent interacting with male or female experimenter skin swabs versus control (water) swabs (CD1 mice; n = 6 experimenters per sex; n = 24 mice per sex; two-sided Wilcoxon matched-pairs signed-rank test; male swabs P = 0.031, female swabs P = 0.031) (c) and test versus habituation in the real-time place preference with experimenter and control t-shirts (CD1 mice; n = 8 experimenters per sex; n = 16 mice per sex; two-sided paired t-test; male t-shirts P < 0.001, female t-shirts P = 0.049) (d). e, Time spent in each arm of a Y-maze with male-, female- and water-scented swabs (CD1 mice; n = 8 experimenters per sex; n = 30 mice; two-sided repeated measures (RM) two-way ANOVA followed by Holm–Sidak correction, P = 0.023). f, Percentage change from habituation (CD1 mice; n = 8 experimenters per sex; n = 30 mice per sex, two-sided Kruskal–Wallis followed by correction with two-stage linear step-up procedure of Benjamini, Krieger and Yekutieli; control versus male Q = 0.001, male versus female Q = 0.010). g, Representative heat maps of mice shown in h. h, Conditioned place preference/aversion (CPP and CPA) of mice with male-scent-paired and female-scent-paired compartments (CD1 mice; n = 8 mice per sex; two-sided Mann–Whitney U test for CPA, P = 0.038; and two-sided unpaired t-test for CPP, P = 0.831). i, ROC curve includes all data in this figure (P = 0.0031). j, Latency to groom in the presence of male or female experimenter skin swabs (CD1 mice; n = 13 experimenters per sex; n = 26 mice per sex; two-sided Kolmogorov–Smirnov test, P = 0.046). k, Latency to eat in the novelty-suppressed feeding test (CD1 mice; n = 7 experimenters per sex; n = 28 mice per sex; two-sided unpaired t-test, P = 0.009). l, Escape failures following inescapable shock training displayed by mice handled by male and female experimenters (CD1 mice; n = 8 experimenters per sex for male mice and n = 8 experimenters per sex for female mice; n = 40 female mice and n = 40 male mice per sex; two-sided RM two-way ANOVA, sex effect P = 0.048; and two-sided Mann–Whitney U test, P = 0.012). m, Contingency analysis of the number of stress-resilient and stress-prone mice (two-sided Fisher’s exact test, P = 0.0018). Data shown are mean ± s.e.m. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001. For detailed statistical information, see Supplementary Table 1. VEH, vehicle.