FIGURE 1.
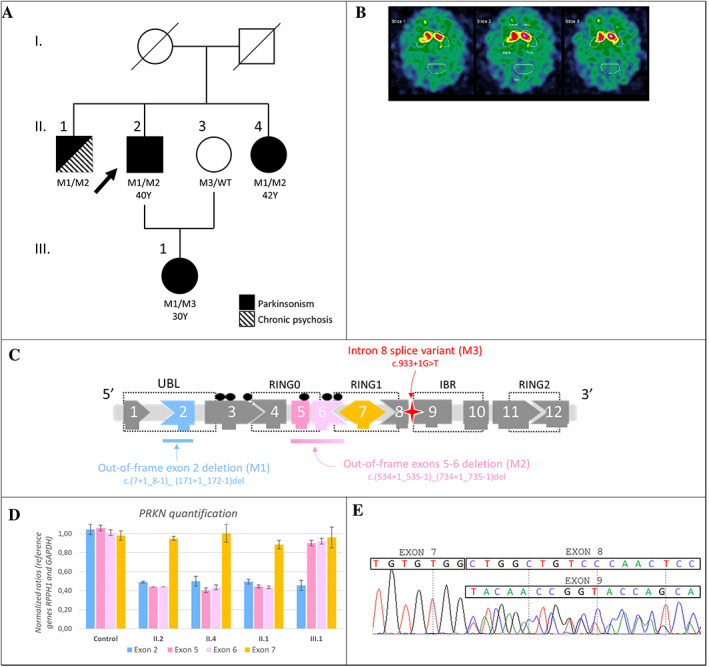
(A) Family pedigree. Black symbols represent affected individuals. The arrow indicates the proband. Mutational status: M1: deletion in exon 2 (NM_004562.2:c.(7+1_8–1)_(171+1_172–1)del), M2: deletion overlapping exons 5 and 6 (NM_004562.2:c.(534+1_535–1)_(734+1_735–1)del), M3: splice variant in intron 8 (NM_004562.2:c.933+1G>T), WT: wild type, Y: age at disease's onset. (B) Datscan imaging of patient III.1 shows bilateral putaminal dopaminergic depletion. (C) PRKN structure and variants identified in the family. UBL: ubiquitin‐like domain; RING: zinc finger domain; IBR: in‐between ring domain; black dots: casein phosphorylation sites. (D) PRKN quantification by qPCR in II.1, II.2, II.4, III.1 and a healthy individual as control. (E) Sanger sequencing on III.1 blood cDNA illustrates heterozygous exon 8 skipping. At the end of exon 7, exon 8 and 9 sequences overlap.
