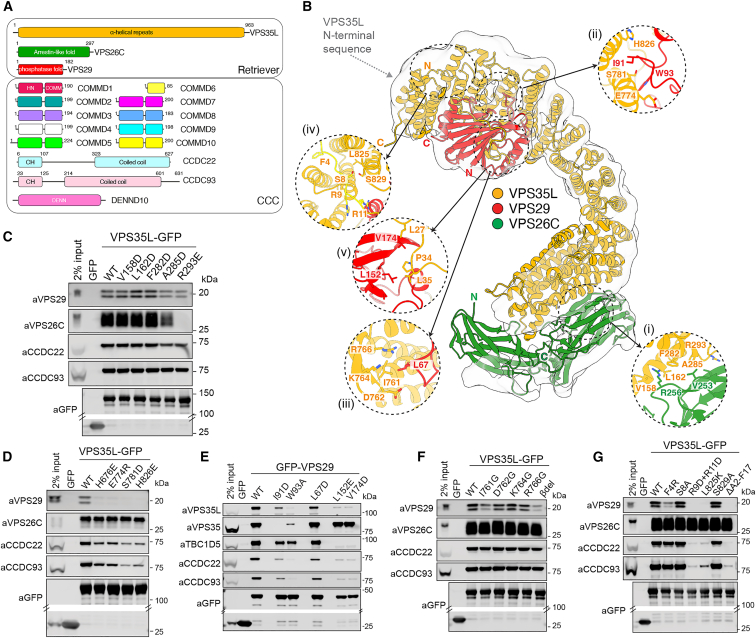
Figure 1.
Architecture of the human Retriever complex
(A) Schematic of Retriever and CCC sub-complexes that form the Commander assembly.
(B) Low resolution cryoEM envelope of human Retriever with docked AlphaFold2 model (Methods S1). Insets show details of: (i). VPS35L:VPS26C interface; (ii). VPS35L:VPS29 interaction; (iii). β-hairpin of VPS35L interacting with VPS29; (iv). intramolecular interaction of N terminus of VPS35L with its C terminus; (v). PL motifs in the N terminus of VPS35L interacting with the hydrophobic surface of VPS29.
(C and D) GFP-nanotrap of GFP-VPS35L mutants targeting the interface with (C) VPS26C and (D) VPS29.
(E) GFP-nanotrap of GFP-VPS29 mutants targeting the major interfaces within Retriever.
(F) GFP-nanotrap of GFP-VPS35L mutants targeting the β-hairpin.
(G) GFP-nanotrap of GFP-VPS35L mutants targeting the N-terminal sequence mediating intramolecular interactions with the VPS35L C terminus. All blots are representative of three independent experiments. Data S1 shows quantified and raw blots (n = 3).
See also Figure S1 and Methods S1.