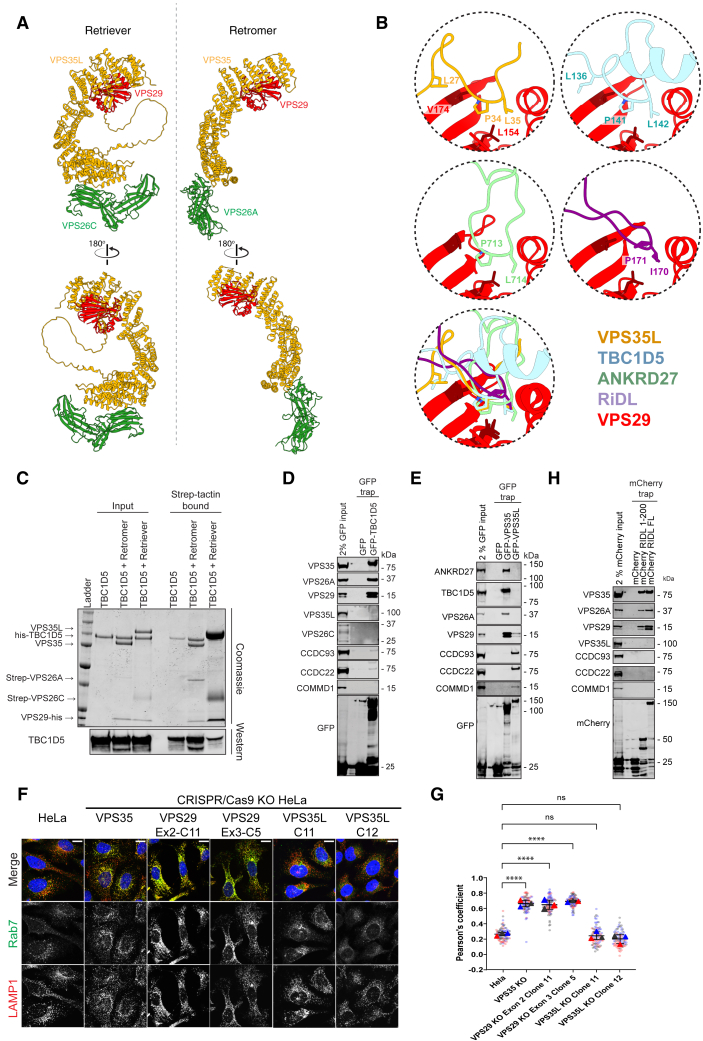
Figure S1.
Comparative architecture of Retriever and Retromer assembly and context specific role of VPS29 in accessory protein binding, related to Figures 1 and 2
(A) Comparison between Retriever and Retromer assemblies.
(B) VPS35L PL motif binding to VPS29 mimics association of Retromer accessory proteins, TBC1D5 (5GTU) and ANKRD27 (6TL0), and the Legionella effector RidL (5WYH) to VPS29.
(C) Recombinant Strep-tagged VPS26A-Retromer and Strep-tagged VPS26C-Retriever were incubated with recombinant his-tagged TBC1D5 and subjected to Strep-tactin affinity isolation. Coomassie staining and Western analysis reveals robust association with Retromer but limited association with Retriever. Representative of two independent experiments.
(D, E, and H) HEK293T cells were transfected with GFP and (D) GFP-TBC1D5, (E) GFP-VPS35 and GFP-VPS35L, and (H) mCherry-RidL (1–200) or full length (FL) RidL and subjected to GFP- or mCherry-nanotrap. Representative of three independent experiments.
(F) VPS35L KO cells do not have elevated lysosomal RAB7 levels. HeLa WT or HeLa KO cells were imaged by confocal microscopy. Scale bars represent 10 μm. Representative images from 3 independent experiments.
(G) Quantification of Pearson’s coefficients between RAB7 and LAMP1 from (F). For each condition, 30 cells were quantified per 3 independent experiments (90 cells total). Pearson’s coefficients for individual cells are represented by transparent circles, colored according to the independent experiment. Error bars represent the mean, S.D. Mean represented by solid triangles, colored by replicate. Normality of data was checked prior to one-way ANOVA followed by Dunnett test for multiple comparisons. ∗∗∗∗ = p < 0.0001, ns = not significant.