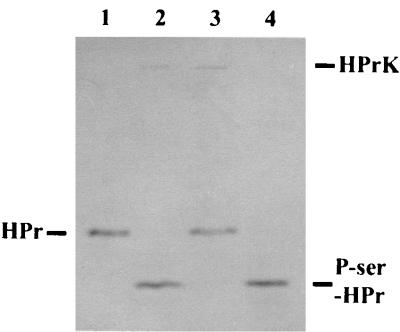
FIG. 2.
HPr kinase and P-Ser-HPr phosphatase activity of purified His6-HPrK enzyme. As substrates, a mutant form of S. aureus HPr, His-15-Ala-HPr, and the P-Ser derivative thereof were applied. HPr and phosphorylated HPr were separated on 15% nondenaturing polyacrylamide gels and visualized by Coomassie blue staining. Lane 1 and 4 (controls), 2 μg of HPr and P-Ser-HPr, respectively; lane 2, 2 μg of HPr and 0.5 μg of His6-HPrK enzyme, incubated in the presence of 5 mM ATP–50 mM Tris (pH 7.5)–50 mM NaCl–10 mM MgCl2 for 20 min at 37°C; lane 3, 2 μg of P-Ser-HPr and 0.5 μg of His6-HPrK enzyme, incubated in the presence of 1 mM NaH2PO4 instead of ATP–50 mM Tris (pH 7.5)–50 mM NaCl–10 mM MgCl2 for 20 min at 37°C. The positions of HPr, P-Ser-HPr, and His6-HPrK on the gel are indicated.