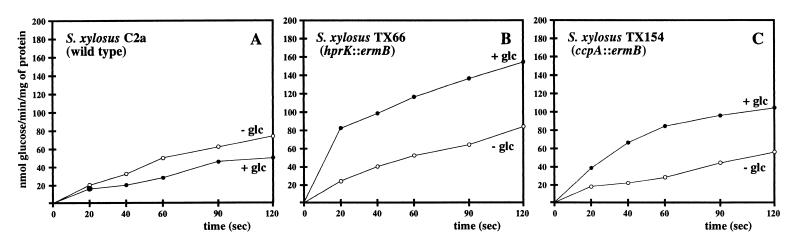
FIG. 5.
Glucose uptake in S. xylosus wild-type C2a, in the hprK mutant TX66, and in the ccpA mutant TX154. (A) Glucose uptake in S. xylosus C2a. The cells were grown in B medium. Glucose was added to a final concentration of 25 mM, when the strains were grown to an OD578 of 1. Glucose uptake was determined after 1 h of further growth, using 200 μM [14C]glucose (6.2 mCi/mmol). The values represent measurements of two cultures. Standard deviations were in the range of ±14%. (B) Glucose uptake in the hprK mutant TX66. The cells were grown in B medium. Glucose was added to a final concentration of 25 mM, when the strains were grown to an OD578 of 1. Glucose uptake was determined after 1 h of further growth, using 200 μM [14C]glucose (6.2 mCi/mmol). The values represent measurements of three cultures. Standard deviations were in the range of ±22%. (C) Glucose uptake in the ccpA mutant TX154. The cells were grown in B medium. Glucose was added to a final concentration of 25 mM, when the strains were grown to an OD578 of 1. Glucose uptake was determined after 1 h of further growth, using 200 μM [14C]glucose (6.2 mCi/mmol). The values represent measurements of three cultures. Standard deviations were in the range of ±16%.