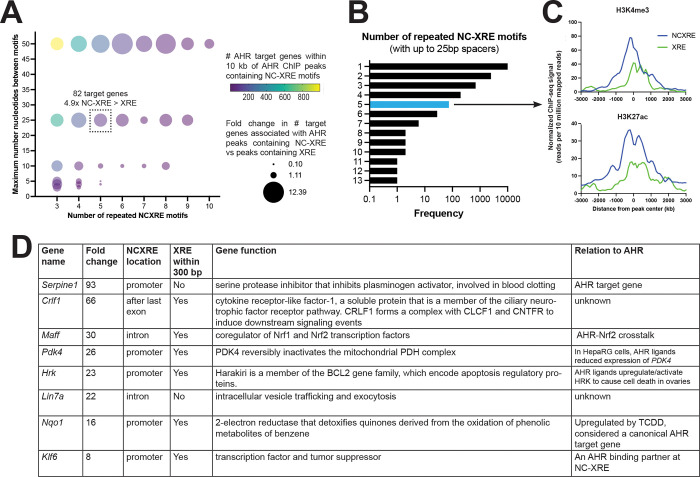
Figure 2. Repeated NC-XRE motifs associated with AHR target genes.
(A) Relative frequency of putative AHR target genes within 10kb of AHR ChIP peaks containing 3–10 NC-XRE motifs with 1–50 basepair (bp) spacers, compared to AHR peaks containing 3–10 XRE motifs with similar spacing. AHR ChIP peaks containing 5 NC-XRE motifs separated by 25 basepairs or less were found within 10 kb of 82 target genes. There are 4.9 fold more AHR target genes associated with AHR ChIP peaks containing 5 NCXRE motifs vs 5 XRE motifs separated by 25 bp or less. (B) Frequency of repeated runs of NCXRE motifs in AHR ChIP peaks. In 24% of AHR ChIP-seq peaks there are 2 or more NCXRE motifs separated by 25 basepairs or less. (C) Binding strength of H3K4me3 and H3K27ac at AHR peaks containing 5 or more NC-XRE or XRE motifs separated by 25 basepairs or less. Runs of NCXRE are enriched at AHR binding sites proximal to transcription start sites, as marked by H3K4me or H3K27ac ChIP peaks. (D) Examples of differentially expressed AHR target genes (fold change TCDD vs vehicle, mouse liver) containing AHR ChIP peaks with 5 or more NC-XRE motifs separated by 25 basepairs or less. We define AHR target genes as differentially expressed genes (RNA-seq, fold difference in TCDD vs vehicle > 1.5x, FDR<5%) containing AHR ChIP peak within 10 kb of a gene body.