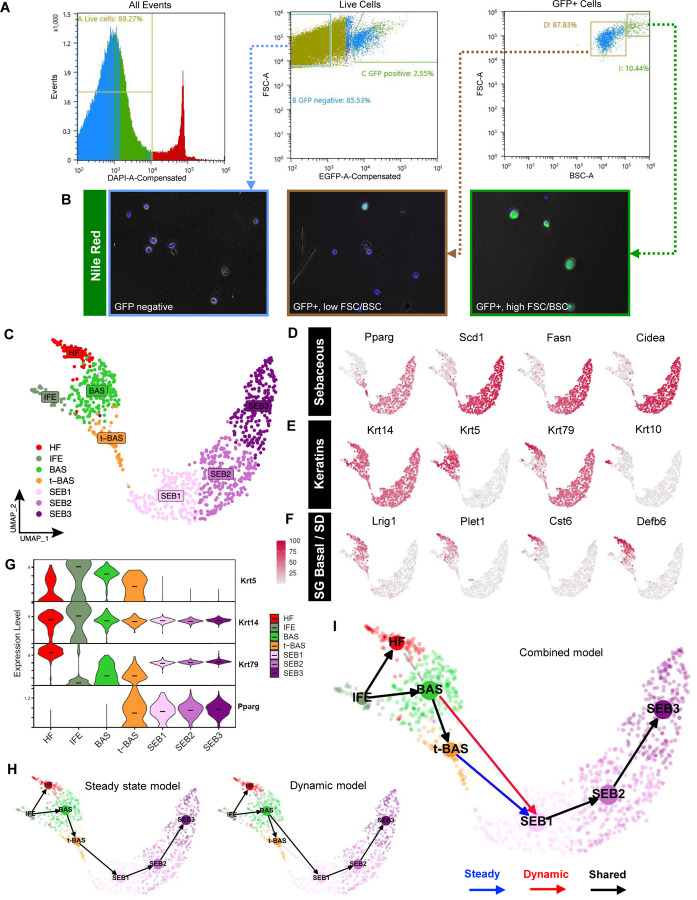
Figure 3. Isolating and profiling SG cells.
A. Flow cytometry plots of isolated cell suspensions from 8 week old PPARγ;YFP skin. B. Nile red staining (green) of sorted keratinocyte subpopulations: bulk GFP negative (left), GFP+ with low FSC/BSC (middle), and GFP+ with high FSC/BSC (right). Note that GFP epifluorescence is not visible and does not interfere with bright Nile red staining, which was superimposed upon bright-field images. C. UMAP projection showing 7 cell clusters isolated from YFP-sorted, 8 week old PPARγ;YFP label-on skin. D. Feature plots for canonical SG genes. E. Feature plots for key keratin genes. F. Feature plots for previously identified markers of SG basal progenitors and sebaceous duct (SD). G. Violin plots showing relative expression of key marker genes across different cell sub-populations. Note that t-BAS cells uniquely express both Krt5 and Pparg. Horizontal lines indicate median values. H. RNA-velocity trajectory analysis performed using either a steady state (left) or dynamic (right) model using scVelo. I. Trajectory analysis incorporating results from both steady state and dynamic models, suggesting that BAS cells enter the transitional t-BAS state before differentiating into SEB-1 sebocytes (blue arrow) or can differentiate directly into SEB-1 sebocytes (red arrow). Black arrows, lineage relationships identified by both models.