Figure 4.
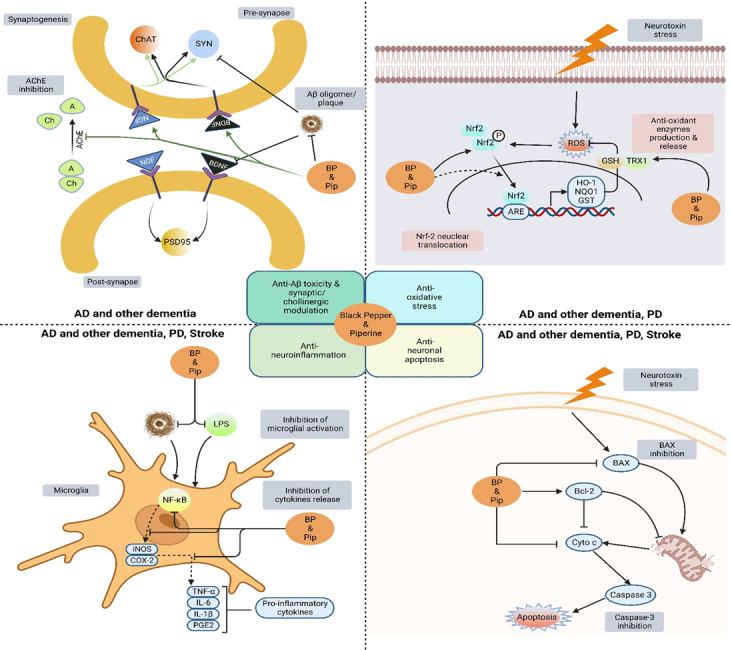
Neuroprotective potential of black pepper and its bioactive compound piperine in age-related neurological disorders. Black pepper and piperine show various neuropharmacological effects via antioxidative stress, anti-neuroinflammation, cholinergic function, anti-Aβ toxicity, anti-neuronal apoptosis, and synaptic function modulation. The block lines () and arrows (→) denote inhibition and stimulation actions by black pepper and piperine, respectively. Key: Aβ, amyloid beta; HO-1, heme oxygenase; Nrf2, nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2; NF-κB, nuclear factor kappa B; ROS, reactive oxygen species; iNOS, inducible nitric oxide synthase; COX-2, cyclooxygenase-2; LPS, lipopolysaccharide; AChE, acetylcholinesterase; IL-1β, interleukin-1β; TNF-α, tumor necrosis factor-α; IL-6, interleukin-6; PSD-95, postsynaptic density protein 95; GSH, glutathione; GPx, glutathione peroxidase; Bcl2, B-cell lymphoma 2.
