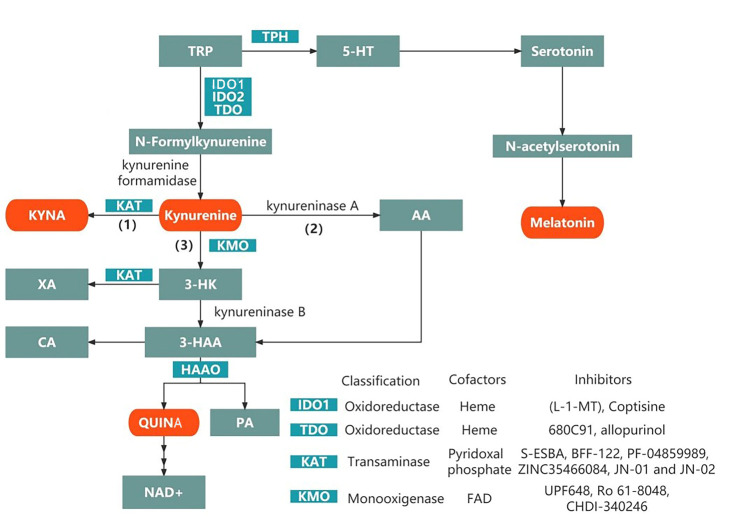
Figure 1.
Tryptophan metabolism by the kynurenine and methoxyindole pathways. Kynurenine is a central KP metabolite capable of degradation through three specific pathways, shown in (1), (2) and (3) in the schematic diagram, to generate different neuroactive metabolites. Abbreviations: TRP, tryptophan; IDO, indoleamine-2,3-dioxygenase; TDO, tryptophan-2,3-dioxygenase; KAT, kynurenine aminotransferase I-III; AA, anthranilic acid; 3-HK, 3-hydroxykynurenine; 3-HAA, 3-hydroxyanthrenillc acid; KMO, kynurenine 3-monooxygenase; HAAO, 3-hydroxyanthranilate 3,4-dioxygenase; KP, kynurenine pathway; KYNA, kynurenic acid; PA, picolinic acid; QUINA, quinolinic acid; TPH, tryptophan hydroxylase; CA, cinnabarinic acid; XA, xanthurenic acid; NAD+, nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide; 5-HT, 5-hydroxytryptophan; TPH, tryptophan hydroxylase.