Table 1.
The primary metabolites in the tryptophan pathway.
| Substances | Structural formula | Functions in the Kynurenine pathway |
|---|---|---|
| TRP |
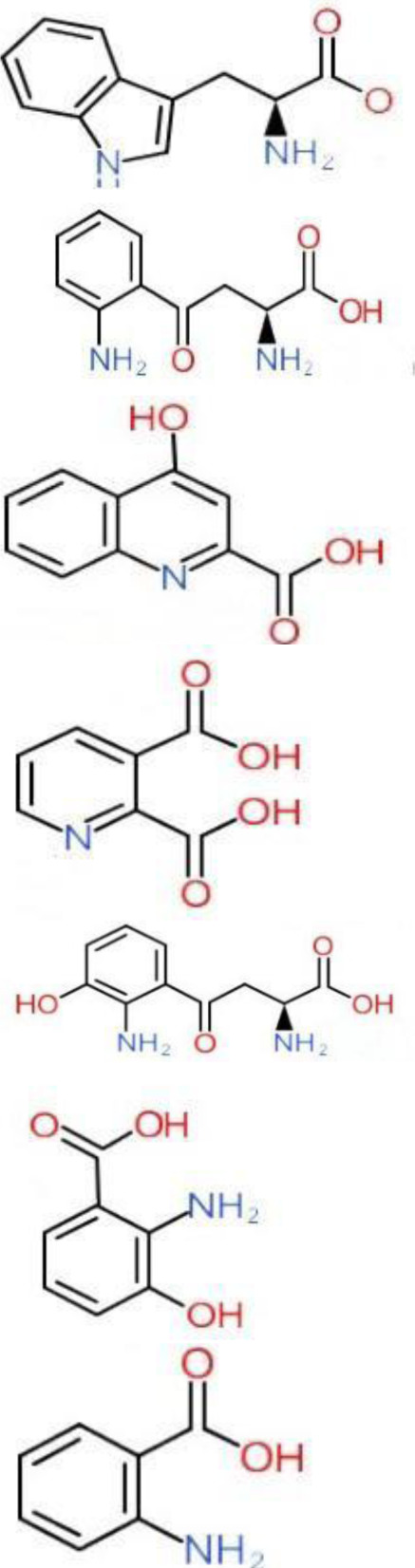
|
The metabolic substrate of KP pathway |
| L-KYN | 1. Neuroprotective effect 2. Immunosuppression, inhibition of the activity of natural killer cells, APC and DC [25] 3. Blocking T-cell proliferation and upregulation of regulatory T cells [43] |
|
| KYNA | 1. Neuroprotective effect 2. A competitive antagonist of NMDA and AMPA [30] 3. Anti-inflammatory effect by stimulating GPR35 [34] 4. Immunosuppressive effect by activating AhR [37] 5. An antioxidant to remove ROS [31] |
|
| QUINA | 1. Neural excitotoxicity [6] 2. Selective activation of NMDA receptors [8] 3. ROS formation and lipid peroxidation [29] 4. BBB disruption [47] 5. Upregulation of nitric oxide synthase and increases in neurotoxicity [93] |
|
| 3-HK | 1. The metabolite of L-KYN catalyzed by KMO 2. Neurotoxic effect 3. Producing free radicals and participating in the metabolism of oxidative stress and fat peroxidation [22] |
|
| 3-HAA | 1. The 3-HK metabolite catalyzed by Kynureninase 2. Neurotoxic effect |
|
| AA | 1. The metabolite of L-KYN catalyzed by Kynureninase 2. Inhibition of 3-HAA metabolism in QUINA and PA, thus exhibiting a neuroprotective effect [161] |
Abbreviations: 3-HAA: 3-hydroxyanthrenillc acid; 3-HK: 3-hydroxykynurenine; AA: anthranilic acid; AhR: aryl hydrocarbon receptor; AMPA: α-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazole-propionic acid; APC: antigen-presenting cells; BBB: blood-brain barrier; DC: dendritic cells; GPR35: G protein-coupled receptor 35; KMO: kynurenine 3-monooxygenase; KP: kynurenine pathway; KYNA: kynurenic acid; L-KYN: L-kynurenine; NMDA: N-methyl-D-aspartic acid; PA: picolinic acid; QUINA: quinolinic acid; ROS: reactive oxygen species; TRP: L-tryptophan.
